相关学习
优先级队列
二叉堆
堆排序
延迟队列
Q
-
是什么?
-
怎么用
-
注意事项?
-
源码
优先级队列
我们知道队列是遵循先进先出(First-In-First-Out)模式的,但有些时候需要在队列中基于优先级处理对象。举个例子,比方说我们有一个每日交易时段生成股票报告的应用程序,需要处理大量数据并且花费很多处理时间。客户向这个应用程序发送请求时,实际上就进入了队列。我们需要首先处理优先客户再处理普通用户。在这种情况下,Java的PriorityQueue(优先队列)会很有帮助。
PriorityQueue类在Java1.5中引入并作为 Java Collections Framework 的一部分。PriorityQueue是基于优先堆的一个无界队列,这个优先队列中的元素可以默认自然排序或者通过提供的Comparator(比较器)在队列实例化的时排序。
优先队列不允许空值,而且不支持non-comparable(不可比较)的对象,比如用户自定义的类。优先队列要求使用Java Comparable和Comparator接口给对象排序,并且在排序时会按照优先级处理其中的元素。
优先队列的头是基于自然排序或者Comparator排序的最小元素。如果有多个对象拥有同样的排序,那么就可能随机地取其中任意一个。当我们获取队列时,返回队列的头对象。
优先队列的大小是不受限制的,但在创建时可以指定初始大小。当我们向优先队列增加元素的时候,队列大小会自动增加。
PriorityQueue是非线程安全的,所以Java提供了PriorityBlockingQueue(实现BlockingQueue接口)用于Java多线程环境。
我们有一个用户类Customer,它没有提供任何类型的排序。当我们用它建立优先队列时,应该为其提供一个比较器对象。
注意
当您使用迭代器时,PriorityQueue 类不保证元素的任何顺序。
它的toString()方法使用它的迭代器给你的元素的字符串表示。
以下代码显示如何使用 Comparator 对象为ComparablePerson列表创建优先级队列。
入门案例
演示如何使用 priority queue
代码
public class Customer {
private int id;
private String name;
public Customer(int i, String n){
this.id=i;
this.name=n;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
- PriorityQueueExample.java
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Random;
public class PriorityQueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//优先队列自然排序示例
Queue<Integer> integerPriorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(7);
Random rand = new Random();
for(int i=0;i<7;i++){
integerPriorityQueue.add(new Integer(rand.nextInt(100)));
}
for(int i=0;i<7;i++){
Integer in = integerPriorityQueue.poll();
System.out.println("Processing Integer:"+in);
}
//优先队列使用示例
Queue<Customer> customerPriorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(7, idComparator);
addDataToQueue(customerPriorityQueue);
pollDataFromQueue(customerPriorityQueue);
}
//匿名Comparator实现
public static Comparator<Customer> idComparator = new Comparator<Customer>(){
@Override
public int compare(Customer c1, Customer c2) {
return (int) (c1.getId() - c2.getId());
}
};
//用于往队列增加数据的通用方法
private static void addDataToQueue(Queue<Customer> customerPriorityQueue) {
Random rand = new Random();
for(int i=0; i<7; i++){
int id = rand.nextInt(100);
customerPriorityQueue.add(new Customer(id, "Pankaj "+id));
}
}
//用于从队列取数据的通用方法
private static void pollDataFromQueue(Queue<Customer> customerPriorityQueue) {
while(true){
Customer cust = customerPriorityQueue.poll();
if(cust == null) break;
System.out.println("Processing Customer with ID="+cust.getId());
}
}
}
优先级队列源码解析
类的定义
public class PriorityQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements java.io.Serializable {}
基础属性
java version “1.8.0_191”
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;
/**
* Priority queue represented as a balanced binary heap: the two
* children of queue[n] are queue[2*n+1] and queue[2*(n+1)]. The
* priority queue is ordered by comparator, or by the elements'
* natural ordering, if comparator is null: For each node n in the
* heap and each descendant d of n, n <= d. The element with the
* lowest value is in queue[0], assuming the queue is nonempty.
*/
transient Object[] queue; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The number of elements in the priority queue.
*/
private int size = 0;
/**
* The comparator, or null if priority queue uses elements'
* natural ordering.
*/
private final Comparator<? super E> comparator;
/**
* The number of times this priority queue has been
* <i>structurally modified</i>. See AbstractList for gory details.
*/
transient int modCount = 0; // non-private to simplify nested class access
构造器
构造器大同小异,调用了公共的初始化方法。
private void initElementsFromCollection(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
// If c.toArray incorrectly doesn't return Object[], copy it.
if (a.getClass() != Object[].class)
a = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length, Object[].class);
int len = a.length;
if (len == 1 || this.comparator != null)
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
if (a[i] == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.queue = a;
this.size = a.length;
}
初始化建立一个小顶堆,就是使用
private void initFromCollection(Collection<? extends E> c) {
initElementsFromCollection(c);
heapify();
}
其中
/**
* Establishes the heap invariant (described above) in the entire tree,
* assuming nothing about the order of the elements prior to the call.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void heapify() {
for (int i = (size >>> 1) - 1; i >= 0; i--)
siftDown(i, (E) queue[i]);
}
核心调整过程
调整,使数据满足小顶堆的结构。
首先介绍两个调整方式siftUp和siftDown
siftDown
在给定初始化元素的时候,要调整元素,使其满足最小堆的结构性质。因此不停地从上到下将元素x的键值与孩子比较并做交换,直到找到元素x的键值小于等于孩子的键值(即保证它比其左右结点值小),或者是下降到叶子节点为止。
例如如下的示意图,调整9这个节点:
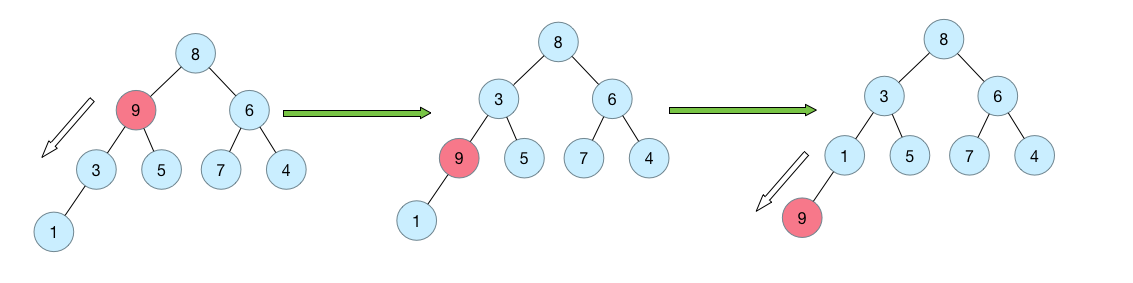
private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x;
int half = size >>> 1; // size/2是第一个叶子结点的下标
//只要没到叶子节点
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1; // 左孩子
Object c = queue[child];
int right = child + 1;
//找出左右孩子中小的那个
if (right < size &&
((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0)
c = queue[child = right];
if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0)
break;
queue[k] = c;
k = child;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
siftUp
priorityQueue 每次新增加一个元素的时候是将新元素插入对尾的。
因此,应该与siftDown有同样的调整过程,只不过是从下(叶子)往上调整。
例如如下的示意图,填加key为3的节点:
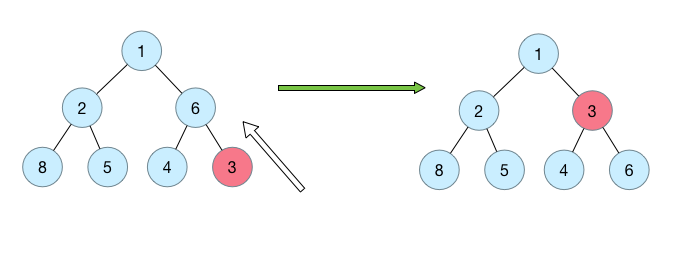
private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x;
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; //获取parent下标
Object e = queue[parent];
if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0)
break;
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
扩容
从实例成员可以看出,PriorityQueue维护了一个Object[], 因此它的扩容方式跟顺序表ArrayList相差不多。
/**
* Increases the capacity of the array.
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// Double size if small; else grow by 50%
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ?
(oldCapacity + 2) :
(oldCapacity >> 1));
// overflow-conscious code
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}
参考资料
http://www.importnew.com/6932.html
《java 并发编程的艺术》
