导读
XmlBeanFactory继承自DefaultListableBeanFactory,扩展了从xml文档中读取bean definition的能力。
从本质上讲,XmlBeanFactory等同于DefaultListableBeanFactory+XmlBeanDefinitionReader,如果有更好的需求,可以考虑使用DefaultListableBeanFactory+XmlBeanDefinitionReader方案,因为该方案可以从多个xml文件读取资源,并且在解析xml上具有更灵活的可配置性。
XmlBeanFactory的使用
构造器
典型构造方法:
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
其中,
reader 是 XmlBeanDefinitionReader的实例,XmlBeanDefinitionReader继承自AbstractBeanDefinitionReader。
Resource 接口封装了各种可能的资源类型,也就是对使用者来说屏蔽了文件类型的不同。
这样所有的资源都被可以通过 InputStream 这个类来获取,所以也屏蔽了资源的提供者。
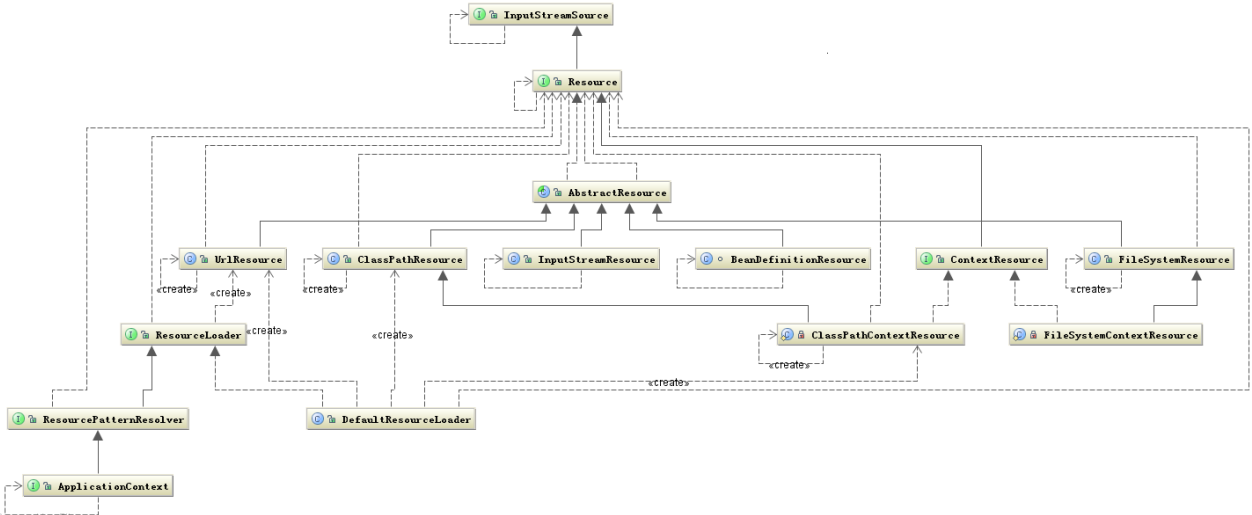
另外还有一个问题就是加载资源的问题,也就是资源的加载者要统一,从上图中可以看出这个任务是由 ResourceLoader 接口完成,他屏蔽了所有的资源加载者的差异,只需要实现这个接口就可以加载所有的资源,他的默认实现是 DefaultResourceLoader。
Resource 接口
Resource 接口继承了 InputStreamSource 接口,这个接口中有个 getInputStream 方法,返回的是 InputStream 类。
定义
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {}
- InputStreamSource.java
public interface InputStreamSource {
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
getInputStream设计希望每次请求都返回一个新的流。
这种要求在一个场合非常重要,例如 javamail api,它在创建多个邮件附件时需要多次读取到流,在这中情况下,它就要求每个getInputStream请求能返回一个新的流。
AbstractResource
抽象资源类 AbstractResource 继承自Source接口,实现了部分方法。
exists方法检查一个文件或者输入量是否可以打开;
isOpen 通常返回false;
getUrl和getFile 抛出异常;
toString返回描述信息。
另外有一个有用的方法:lastModified()返回文件的最后修改时间。
调用了 File.lastModified() 返回此抽象路径名表示的文件最后一次被修改的时间。
/**
* This implementation checks the timestamp of the underlying File,
* if available.
* @see #getFileForLastModifiedCheck()
*/
@Override
public long lastModified() throws IOException {
long lastModified = getFileForLastModifiedCheck().lastModified();
if (lastModified == 0L) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() +
" cannot be resolved in the file system for resolving its last-modified timestamp");
}
return lastModified;
}
Resource的实现子类
AbstractResource的直接子类有:AbstractFileResolvingResource, ByteArrayResource,BeanDefinitionResource, DescriptiveResource, FileSystemResource, InputStreamResource, PathResource, VfsResource。
其中,AbstractFileResolvingResource的直接子类有:ClassPathResource, PortletContextResource, ServletContextResource, UrlResource 比较重要的实现类为实现了ContextResource接口的资源类,ContextResource接口继承了Resource接口,通过从一个封装的context中加载资源来扩展Resource接口的功能。
例如:可以从ServletContext,PortletContext,普通的classpth路径或者文件系统的相对路径(特别是没有指明前缀,因此适用于本地ResourceLoader的context),其子类实现有:PortletContextResource, ServletContextResource,ClassPathContextResource,ClassRelativeContextResource,FileSystemContextResource。
资源的加载 ResourceLoader
ResourceLoader是一个加载资源的策略接口,可以从classpth或者文件系统中,ApplicationContext需要加载资源功能,使用了其扩展类ResourcePatternReolver。
DefaultResourceLoader是该接口的标准实现,适用于一个ApplicationContext外部,可以用在ResourceEditor中。
在application允许过程中,使用特定的context子原因加载策略,可以将type资源和资源组通过string的形式设置bean的属性。
Bean 的解析与注册详细过程分析

首先, XmlBeanFactory构造函数this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
-
XmlBeanDefinitionReader加载bean定义:loadBeanDefinitions方法
-
XmlBeanDefinitionReader解析bean定义,并注册:doLoadBeanDefinitions方法
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
整体流程
标准加载到 document
使用标准的JAXP配置的xml解析器从Resource中加载到Document。
/**
* Load the {@link Document} at the supplied {@link InputSource} using the standard JAXP-configured
* XML parser.
*/
@Override
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}
根据加载的Document 注册Bean definition。
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
documentReader.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
-
创建BeanDefinitionDocument的解析器BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.documentReaderClass)
-
BeanDefinitionDocument解析器注册bean definition,从根节点
<beans>开始
/**
* Register each bean definition within the given root {@code <beans/>} element.
*/
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
return;
}
}
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(this.readerContext, root, parent);
preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
- parseBeanDefinitions.java
/**
* Parse the elements at the root level in the document:
* "import", "alias", "bean".
* @param root the DOM root element of the document
*/
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
注册
registerBeanDefinitions 注册 bean 属性
/**
* Register the bean definitions contained in the given DOM document.
* Called by {@code loadBeanDefinitions}.
* <p>Creates a new instance of the parser class and invokes
* {@code registerBeanDefinitions} on it.
* @param doc the DOM document
* @param resource the resource descriptor (for context information)
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of parsing errors
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions
* @see #setDocumentReaderClass
* @see BeanDefinitionDocumentReader#registerBeanDefinitions
*/
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
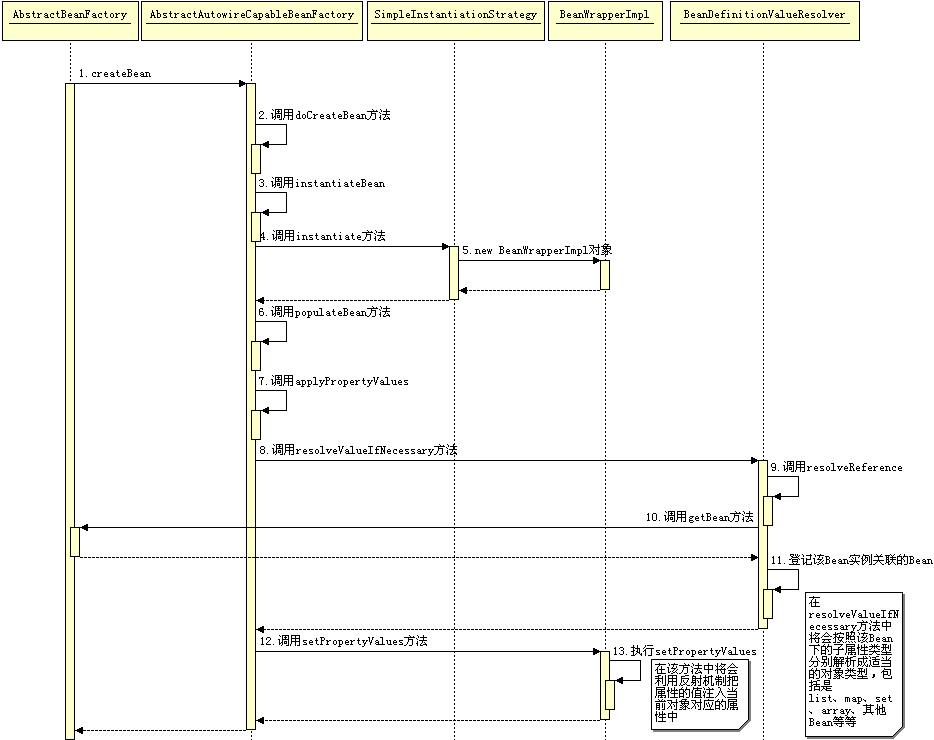
建立关系
一个非常重要的部分就是建立 Bean 对象实例之间的关系,这也是 Spring 框架的核心竞争力,何时、如何建立他们之间的关系请看下面的时序图:
小结:
从spring 3.1版本后,xmlBeanFactory被表明为Deprecated. 推荐使用DefaultListableBeanFactory和XmlBeanDefinitionReader替换。
本文从xmlBeanFactory扩展到XmlBeanDefinitionReader,再到Resource接口。
