42. Trapping Rain Water
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it can trap after raining.
Ex
Example 1:

Input: height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
Output: 6
Explanation: The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.
Example 2:
Input: height = [4,2,0,3,2,5]
Output: 9
Constraints:
n == height.length
1 <= n <= 2 * 10^4
0 <= height[i] <= 10^5
解题思路
看完一脸懵。
还是看看别人的思路。
Solution 1: Max Left, Max Right So Far!
思路
A ith bar can trap the water if and only if there exists a higher bar to the left and a higher bar to the right of ith bar.
To calculate how much amount of water the ith bar can trap, we need to look at the maximum height of the left bar and the maximum height of the right bar, then
1) The water level can be formed at ith bar is: waterLevel = min(maxLeft[i], maxRight[i])
2) If waterLevel >= height[i] then ith bar can trap waterLevel - height[i] amount of water.
To achieve in O(1) when looking at the maximum height of the bar on the left side and on the right side of ith bar, we pre-compute it:
1) Let maxLeft[i] is the maximum height of the bar on the left side of ith bar.
2) Let maxRight[i] is the maximum height of the bar on the right side of ith bar.
要理解这个算法,一共就几个关键点。
1) ith 位置什么情况下可以存水?
只能当左边存在一个较高的 bar,且右边也存在一个较高的 bar。
这样中间才能形成低洼存水。
2)ith 位置能存多少水呢?
我们要去计算 ith 位置,对应的水位线。
水位线,肯定是 min(maxLeft, maxRight)。木桶原理,水位线最多和低的一个 bar 持平。
ith 和水位线直接对比,如果小于水位线就可以存水。
存水 = 水位线 - ith.val
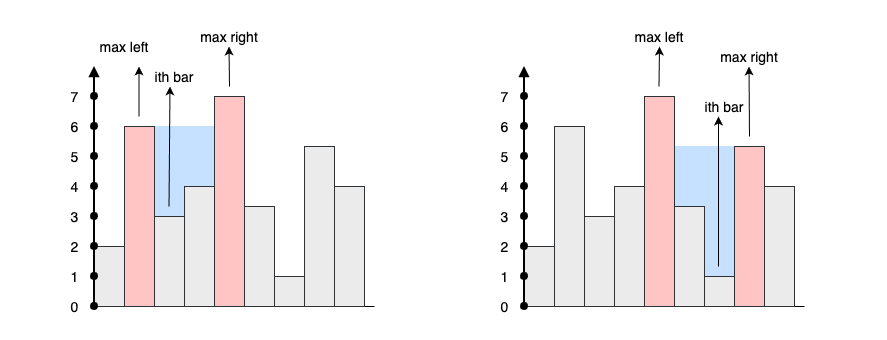
问题的本质
这样的话,问题就变成了我们如何计算 i 这个位置,左边和右边的最大值。
使用 2 个数组,leftArray, rightArray 分别记录每一个位置的最大高度。
java 实现
/**
* @author d
* @since 1.0.0
*/
public class T042_TrappingRainWater {
/**
* 计算
*
* 1. 两个数组保存两边的高度
*
* 2. 循环计算
*
* @param height 高度
* @return 结果
*/
public int trap(int[] height) {
int n = height.length;
//1. 最大高低数组
int[] leftMax = new int[n];
int[] rightMax = new int[n];
//1.1 左边 从左到右
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
leftMax[i] = Math.max(height[i-1], leftMax[i-1]);
}
//1.2 右边 从右到左
for(int i = n-2; i >= 0; i--) {
rightMax[i] = Math.max(height[i+1], rightMax[i+1]);
}
//2. 遍历计算
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int waterLevel = Math.min(leftMax[i], rightMax[i]);
sum += Math.max(0, waterLevel - height[i]);
}
return sum;
}
}
1ms, beats 99%。
TC: O(N), where N <= 3*10^4 is number of bars.
SC: O(N)
非常便于理解的算法。
Solution 2: Two Pointers
算法
Same idea with solution 1, but now we don't need to build maxLeft and maxRight arrays, we will calculate maxLeft and maxRight as we go.
We start with maxLeft = height[0], maxRight = height[n-1], using 2 pointers left point to the next bar on the left side, right point to the next bar on the right side.
How to decide to move left or move right?
If maxLeft < maxRight, it means the water level is based on the left side (the left bar is smaller) then move left side:
If height[left] > maxLeft then there is no trap water, we update maxLeft by maxLeft = height[left].
Else if height[left] < maxLeft then it can trap an amount of water, which is maxLeft - height[left].
Move left by left += 1
Else if maxLeft > maxRight, it means the water level is based on the right side (the right bar is smaller) then move right side:
If height[right] > maxRight then there is no trap water, we update maxRight by maxRight = height[right].
Else if height[right] < maxRight then it can trap an amount of water, which is maxRight - height[right].
Move right by right -= 1.
这个和 T11-container-with-most-water 的策略比较类似。
和解法1类似,但是不需要构建 2 个额外的数组,而是在遍历的时候计算出来。
初始值:maxLeft = height[0], maxRight = height[n-1]
使用双指针 left、right。如何决定移动呢?
1) maxLeft 小于 maxRight
水位线取决于低的,也就是左边。
if(height[left] > maxLeft) {
// 无法蓄水
maxLeft = height[left];
} else {
// 可以蓄水
int water = maxLeft - height[left];
}
// 左边指针往右移动
left++;
2) maxLeft 大于 maxRight
水位线取决于低的,也就是右边。
if(height[right] > maxRight) {
// 无法蓄水
maxRight = height[right];
} else {
// 可以蓄水
int water = maxRight - height[right];
}
// 右边指针往左移动
right--;
java 实现
/**
* @author d
* @since 1.0.0
*/
public class T042_TrappingRainWaterV2 {
/**
* 计算
*
* 1. 通过双指针,实时计算
*
* @param height 高度
* @return 结果
*/
public int trap(int[] height) {
int n = height.length;
//1. 最大高度
int left = 0;
int right = n-1;
int maxLeft = height[left];
int maxRight = height[right];
int sum = 0;
while (left <= right) {
// 取决于左边
if(maxLeft < maxRight) {
if(height[left] > maxLeft) {
// 无法蓄水
maxLeft = height[left];
} else {
// 可以蓄水
sum += maxLeft - height[left];
}
// 左边指针往右移动
left++;
} else {
// 取决于右边
if(height[right] > maxRight) {
// 无法蓄水
maxRight = height[right];
} else {
// 可以蓄水
sum += maxRight - height[right];
}
// 右边指针往左移动
right--;
}
}
return sum;
}
}
Complexity
TC: O(N), where N <= 3*10^4 is number of bars.
SC: O(1)
参考资料
https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/description/
https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/solutions/17357/sharing-my-simple-c-code-o-n-time-o-1-space/
https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/solutions/17391/share-my-short-solution/
https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/solutions/153992/java-o-n-time-and-o-1-space-with-explanations/
https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/solutions/1374608/c-java-python-maxleft-maxright-so-far-with-picture-o-1-space-clean-concise/
