模块化开发概述
SOFABoot 从 2.4.0 版本开始支持基于 Spring 上下文隔离的模块化开发能力。为了更好的理解 SOFABoot 模块化开发的概念,我们来区分几个常见的模块化形式:
基于代码组织上的模块化:这是最常见的形式,在开发期,将不同功能的代码放在不同 Java 工程下,在编译期被打进不同 jar 包,在运行期,所有 Java 类都在一个 classpath 下,没做任何隔离;
基于 Spring 上下文隔离的模块化:借用 Spring 上下文来做不同功能模块的隔离,在开发期和编译期,代码和配置也会分在不同 Java 工程中,但在运行期,不同模块间的 Spring Bean 相互不可见,DI 只在同一个上下文内部发生,但是所有的 Java 类还是在同一个 ClassLoader 下;
基于 ClassLoader 隔离的模块化:借用 ClassLoader 来做隔离,每个模块都有独立的 ClassLoader,模块与模块之间的 classpath 不同,SOFAArk 就是这种模块化的实践方式。
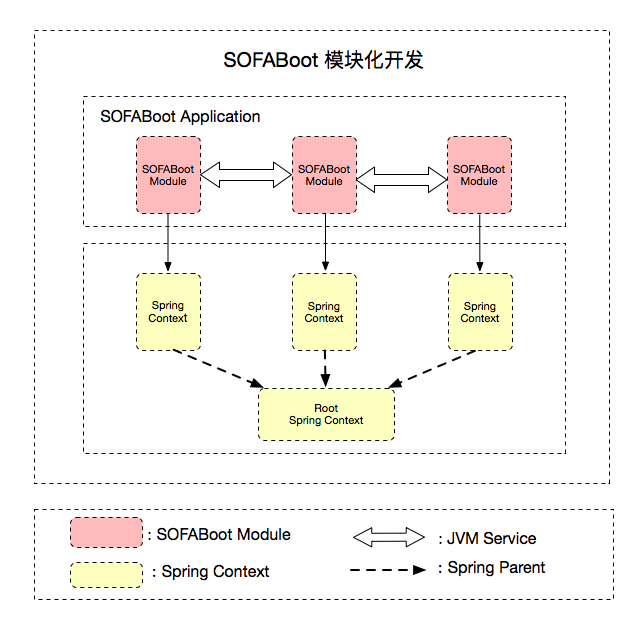
SOFABoot 模块化开发属于第二种模块化形式 —— 基于 Spring 上下文隔离的模块化。
每个 SOFABoot 模块使用独立的 Spring 上下文,避免不同 SOFABoot 模块间的 BeanId 冲突,有效降低企业级多模块开发时团队间的沟通成本。
关于 SOFABoot 模块化产生的背景,可参考文章 《蚂蚁金服的业务系统模块化 —- 模块化隔离方案》
功能简介
依赖引入
使用 SOFABoot 模块化开发方案,需要引入如下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alipay.sofa</groupId>
<artifactId>isle-sofa-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
SOFABoot 模块
SOFABoot 框架定义了 SOFABoot 模块的概念,一个 SOFABoot 模块是一个包括 Java 代码、Spring 配置文件、SOFABoot 模块标识等信息的普通 Jar 包,一个 SOFABoot 应用可以包含多个 SOFABoot 模块,每个 SOFABoot 模块都含有独立的 Spring 上下文。
以 SOFABoot 模块为单元的模块化方式为开发者提供了以下功能:
-
运行时,每个 SOFABoot 模块的 Spring 上下文是隔离的,模块间定义的 Bean 不会相互影响;
-
每个 SOFABoot 模块是功能完备且自包含的,可以很容易在不同的 SOFABoot 应用中进行模块迁移和复用,只需将 SOFABoot 模块整个拷贝过去,调整 Maven 依赖,即可运行。
SOFABoot 模块的格式定义见: 模块配置。
SOFABoot 模块间通信
上下文隔离后,模块与模块间的 Bean 无法直接注入,模块间需要通过 SOFA 服务进行通信,目前SOFABoot 提供了两种形式的服务发布和引用,用于解决不同级别的模块间调用的问题:
-
JVM 服务发布和引用:解决一个 SOFABoot 应用内部各个 SOFABoot 模块之间的调用问题, JVM 服务发布与引用
-
RPC 服务发布和引用:解决多个 SOFABoot 应用之间的远程调用问题,RPC 服务发布与引用。
模块并行化启动
每个 SOFABoot 模块都是独立的 Spring 上下文,多个 SOFABoot 模块支持并行化启动,与 Spring Boot 的单 Spring 上下文模式相比,模块并行化启动能够加快应用的启动速度。
Root Application Context
SOFABoot 应用运行时,本身会产生一个 Spring Context,我们把它叫做 Root Application Context,它是每个 SOFABoot 模块创建的 Spring Context 的 Parent。这样设计的目的是为了保证每个 SOFABoot 模块的 Spring Context 都能发现 Root Application Context 中创建的 Bean,这样当应用新增 Starter 时,不仅 Root Application Context 能够使用 Starter 中新增的 Bean,每个 SOFABoot 模块的 Spring Context 也能使用这些 Bean。
模块配置
SOFABoot 模块是一个普通的 Jar 包加上一些 SOFABoot 特有的配置,这些 SOFABoot 特有的配置,让一个 Jar 包能够被 SOFABoot 识别,使之具备模块化的能力。
一个完整的 SOFABoot 模块和一个普通的 Jar 包有两点区别:
-
SOFABoot 模块包含一份 sofa-module.properties 文件,这份文件里面定义了 SOFABoot 模块的名称以及模块之间的依赖关系。
-
SOFABoot 模块的 META-INF/spring 目录下,可以放置任意多的 Spring 配置文件,SOFABoot 会自动把它们作为本模块的 Spring 配置加载起来。
sofa-module.properties 文件详解
先来看一份完整的 sofa-module.properties 文件(src/main/resources 目录下):
Module-Name=com.alipay.test.biz.service.impl
Spring-Parent=com.alipay.test.common.dal
Require-Module=com.alipay.test.biz.shared
Module-Profile=dev
Module-Name
Module-Name 是 SOFABoot 模块的名称,也是 SOFABoot 模块的唯一标示符。在一个 SOFABoot 应用中,一个 SOFABoot 模块的 Module-Name 必须和其他的 SOFABoot 模块的 Module-Name 不一样。需要注意的一点是,一个 SOFABoot 应用运行时的 SOFABoot 模块,不仅仅只包含本应用的模块,还包括依赖了其他应用的 SOFABoot 模块,确定是否唯一的时候需要把这些 SOFABoot 模块也考虑进去。
Require-Module
Require-Module 用于定义模块之间的依赖顺序,值是以逗号分隔的 SOFABoot 模块名列表,比如上面的配置中,就表示本模块依赖于 com.alipay.test.biz.shared 模块。对于这种依赖关系的处理,SOFABoot 会将 com.alipay.test.biz.shared 模块在本模块之前启动,即com.alipay.test.biz.shared 模块将先启动 Spring 上下文。
一般情况下,是不需要为模块定义 Require-Module 的,只有当模块的 Spring 上下文的启动依赖于另一个模块的 Spring 上下文的启动时,才需要定义 Require-Module。举一个例子,如果你在 A 模块中发布了一个 SOFA JVM Service。在 B 模块的某一个 Bean 的 init 方法里面,需要使用 SOFA Reference 调用这个 JVM Service。假设 B 模块在 A 模块之前启动了,那么 B 模块的 Bean 就会因为 A 模块的 JVM Service 没有发布而 init 失败,导致 Spring 上下文启动失败。这个时候,我们就可以使用 Require-Module 来强制 A 模块在 B 模块之前启动。
Spring-Parent
在 SOFABoot 应用中,每一个 SOFABoot 模块都是一个独立的 Spring 上下文,并且这些 Spring 上下文之间是相互隔离的。虽然这样的模块化方式可以带来诸多好处,但是,在某些场景下还是会有一些不便,这个时候,你可以通过 Spring-Parent 来打通两个 SOFABoot 模块的 Spring 上下文。Spring-Parent 属性可以配置一个模块的名称,比如上面的配置中,就将 com.alipay.test.common.dal 的 Spring 上下文设置为当前模块的 Spring 上下文的父 Spring 上下文。
由于 Spring 的限制,一个模块的 Spring-Parent 只能有一个模块
关于 Spring 的父上下文的作用可以看 Spring 的 BeanFactory 的说明:http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/javadoc-api/org/springframework/beans/factory/BeanFactory.html
Module-Profile
支持 SOFABoot Profile 能力: SOFABoot Profile
Spring 配置文件
SOFABoot 模块可以包含 Spring 配置文件,配置文件需要放置在 META-INF/spring 目录下,SOFABoot 启动时会自动扫描该目录,并把目录下所有 XML 文件作为本模块的 Spring 配置加载起来。
在 Spring 配置文件中,我们可以定义 Bean、发布服务等等。
SOFABoot 模块一般用于封装对外发布服务接口的具体实现,属于业务层,Controller 属于展现层内容,我们不建议也不支持在 SOFABoot 模块中定义 Controller 组件,Controller 组件相关定义请直接放在 Root Application Context。
JVM 服务发布与引用
SOFABoot 提供三种方式给开发人员发布和引用 JVM 服务
-
XML 方式
-
Annotation 方式
-
编程 API 方式
XML 方式
服务发布
首先需要定义一个 Bean:
<bean id="sampleService" class="com.alipay.sofa.runtime.test.service.SampleServiceImpl">
然后通过 SOFA 提供的 Spring 扩展标签来将上面的 Bean 发布成一个 SOFA JVM 服务。
<sofa:service interface="com.alipay.sofa.runtime.test.service.SampleService" ref="sampleService">
<sofa:binding.jvm/>
</sofa:service>
上面的配置中的 interface 指的是需要发布成服务的接口,ref 指向的是需要发布成 JVM 服务的 Bean,至此,我们就已经完成了一个 JVM 服务的发布。
服务引用
使用 SOFA 提供的 Spring 扩展标签引用服务:
<sofa:reference interface="com.alipay.sofa.runtime.test.service.SampleService" id="sampleServiceRef">
<sofa:binding.jvm/>
</sofa:reference>
上面的配置中的 interface 是服务的接口,需要和发布服务时配置的 interface 一致。
id 属性的含义同 Spring BeanId。
上面的配置会生成一个 id 为 sampleServiceRef 的 Spring Bean,你可以将 sampleServiceRef 这个 Bean 注入到当前 SOFABoot 模块 Spring 上下文的任意地方。
service/reference 标签还支持 RPC 服务发布,相关文档: RPC 服务发布与引用
Annotation 方式
如果一个服务已经被加上了 @SofaService 的注解,它就不能再用 XML 的方式去发布服务了,选择一种方式发布服务,而不是两种混用。
除了通过 XML 方式发布 JVM 服务和引用之外,SOFABoot 还提供了 Annotation 的方式来发布和引用 JVM 服务。
通过 Annotation 方式发布 JVM 服务,只需要在实现类上加一个 @SofaService 注解即可,如下:
@SofaService
public class SampleImpl implements SampleInterface {
public void test() {
}
}
- 提示
@SofaService 的作用是将一个 Bean 发布成一个 JVM 服务,这意味着虽然你可以不用再写 <sofa:service/> 的配置,但是还是需要事先将 @SofaService 所注解的类配置成一个 Spring Bean。
在使用 XML 配置 <sofa:service/> 的时候,我们配置了一个 interface 属性,但是在使用 @SofaService 注解的时候,却没有看到有配置服务接口的地方。
这是因为当被 @SofaService 注解的类只有一个接口的时候,框架会直接采用这个接口作为服务的接口。
当被 @SofaService 注解的类实现了多个接口时,可以设置 @SofaService 的 interfaceType 字段来指定服务接口,比如下面这样:
@SofaService(interfaceType=SampleInterface.class)
public class SampleImpl implements SampleInterface, Serializable {
public void test() {
}
}
和 @SofaService 对应,Sofa 提供了 @SofaReference 来引用一个 JVM 服务。
假设我们需要在一个 Spring Bean 中使用 SampleJvmService 这个 JVM 服务,那么只需要在字段上加上一个 @SofaReference 的注解即可:
public class SampleServiceRef {
@SofaReference
private SampleService sampleService;
}
和 @SofaService 类似,我们也没有在 @SofaReference 上指定服务接口,这是因为 @SofaReference 在不指定服务接口的时候,会采用被注解字段的类型作为服务接口,你也可以通过设定 @SofaReference 的 interfaceType 属性来指定:
public class SampleServiceRef {
@SofaReference(interfaceType=SampleService.class)
private SampleService sampleService;
}
使用 @SofaService 注解发布服务时,需要在实现类上打上 @SofaService 注解;在 Spring Boot 使用 Bean Method 创建 Bean 时,会导致 @Bean 和 @SofaService 分散在两处,而且无法对同一个实现类使用不同的 unique id。
因此自 SOFABoot v2.6.0 及 v3.1.0 版本起,支持 @SofaService 作用在 Bean Method 之上,例如:
@Configuration
public class SampleSofaServiceConfiguration {
@Bean("sampleSofaService")
@SofaService(uniqueId = "service1")
SampleService service() {
return new SampleServiceImpl("");
}
}
同样为了方便在 Spring Boot Bean Method 使用注解 @SofaReference 引用服务,自 SOFABoot v2.6.0 及 v3.1.0 版本起,支持在 Bean Method 参数上使用 @SofaReference 注解引用 JVM 服务,例如:
@Configuration
public class MultiSofaReferenceConfiguration {
@Bean("sampleReference")
TestService service(@Value("$spring.application.name") String appName,
@SofaReference(uniqueId = "service") SampleService service) {
return new TestService(service);
}
}
编程 API 方式
SOFABoot 为 JVM 服务的发布和引用提供了一套编程 API 方式,方便直接在代码中发布和引用 JVM 服务,与 Spring 的 ApplicationContextAware 类似,为使用编程 API 方式,首先需要实现 ClientFactoryAware 接口获取编程组件 API:
public class ClientFactoryBean implements ClientFactoryAware {
private ClientFactory clientFactory;
@Override
public void setClientFactory(ClientFactory clientFactory) {
this.clientFactory = clientFactory;
}
}
以 SampleService 为例,看下如何使用 clientFactory 通过编程 API 方式发布 JVM 服务:
ServiceClient serviceClient = clientFactory.getClient(ServiceClient.class);
ServiceParam serviceParam = new ServiceParam();
serviceParam.setInstance(new SampleServiceImpl());
serviceParam.setInterfaceType(SampleService.class);
serviceClient.service(serviceParam);
上面的代码中
-
首先通过 clientFactory 获得 ServiceClient 对象
-
然后构造 ServiceParam 对象,ServiceParam 对象包含发布服务所需参数,通过 setInstance 方法来设置需要被发布成 JVM 服务的对象,setInterfaceType- 来 设置服务的接口
-
最后,调用 ServiceClient 的 service 方法,发布一个 JVM 服务
通过编程 API 方式引用 JVM 服务的代码也是类似的:
ReferenceClient referenceClient = clientFactory.getClient(ReferenceClient.class);
ReferenceParam<SampleService> referenceParam = new ReferenceParam<SampleService>();
referenceParam.setInterfaceType(SampleService.class);
SampleService proxy = referenceClient.reference(referenceParam);
同样,引用一个 JVM 服务只需从 ClientFactory 中获取一个 ReferenceClient ,然后和发布一个服务类似,构造出一个 ReferenceParam,然后设置好服务的接口,最后调用 ReferenceClient 的 reference 方法即可。
通过动态客户端创建的 Reference 对象是一个非常重的对象,请大家在使用的时候不要频繁创建,自行做好缓存,否则可能存在内存溢出的风险。
除了实现 ClientFactoryAware 接口用于获取 ServiceClient 和 ReferenceClient 对象,还可以使用简便的注解 @SofaClientFactory 获取编程 API,例如
public class ClientBean {
@SofaClientFactory
private ReferenceClient referenceClient;
@SofaClientFactory
private ServiceClient serviceClient;
}
uniqueId
有些时候,针对一个接口,我们会需要发布两个服务出来,分别对应到不同的实现。
继续前面的 sampleService 的例子,我们可能有两个 SampleService 的实现,这两个实现我们都需要发布成 SOFA 的 JVM Service,按照前面的教程,采用 XML 的方式,我们就可能用下面这种方式进行配置:
<sofa:service interface="com.alipay.sofa.runtime.test.service.SampleService" ref="sampleService1">
</sofa:service>
<sofa:service interface="com.alipay.sofa.runtime.test.service.SampleService" ref="sampleService2">
</sofa:service>
上面的服务发布没有什么问题,但是当需要引用服务的时候,就出现了问题了,例如我们使用以下配置:
<sofa:reference interface="com.alipay.sofa.runtime.test.service.SampleService" id="sampleService">
</sofa:reference>
这个 JVM 引用到底引用的是哪个 JVM 服务呢,我们无从知晓。
为了解决上面的这种问题,SOFABoot 引入了 uniqueId 的概念,针对服务接口一样的 JVM 服务,可以通过 uniqueId 来进行区分,上面的服务发布的代码我们加入 uniqueId 后,我们可以改成下面这样:
<sofa:service interface="com.alipay.sofa.runtime.test.service.SampleService" ref="sampleService1" unique-id="ss1">
</sofa:service>
<sofa:service interface="com.alipay.sofa.runtime.test.service.SampleService" ref="sampleService2" unique-id="ss2">
</sofa:service>
然后,在引用服务的时候,如果我们要使用 sampleService1 的服务,可以指定 unique-id 为 ss1,比如:
<sofa:reference interface="com.alipay.sofa.runtime.test.service.SampleService" id="sampleService" unique-id="ss1">
</sofa:reference>
如果要使用 sampleService2 的服务,可以指定 unique-id 为 ss2,比如:
<sofa:reference interface="com.alipay.sofa.runtime.test.service.SampleService" id="sampleService" unique-id="ss2">
</sofa:reference>
上面说的是在 XML 的方式中使用 uniqueId。当你用 Annotation 的方式发布 JVM 服务和引用的时候,可以通过设置 @SofaService 和 @SofaReference 的 uniqueId 属性来设置 uniqueId。
当你用编程 API 的方式发布或者引用 JVM 服务的时候,可以通过 ServiceParam 和 ReferenceParam 的 setUniqueId 方法来设置 uniqueId。
模块并行化启动
SOFABoot 会根据 Require-Module 计算模块依赖树,例如以下依赖树表示模块B 和模块C 依赖模块A,模块E 依赖模块D,模块F 依赖模块E:
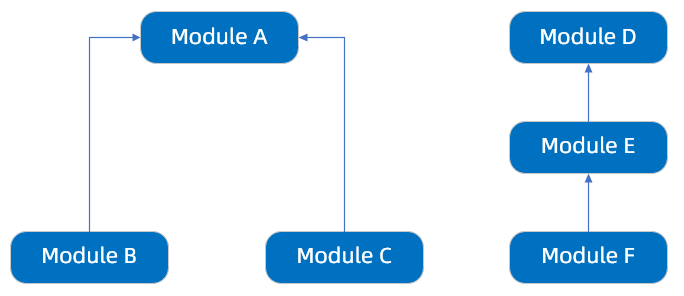
该依赖树会保证模块A 必定在模块B 和模块C 之前启动,模块D 在模块E 之前启动,模块E 在模块F 之前启动,但是依赖树没有定义模块B 与模块C,模块B、C与模块D、E、F之间的启动顺序,这几个模块之间可以串行启动,也可以并行启动。
SOFABoot 默认会并行启动模块,在使用过程中,如果希望关闭并行启动,可以在 application.properties 中增加以下参数:
com.alipay.sofa.boot.module-start-up-parallel=false
Spring Bean 异步初始化
SOFABoot 提供了模块并行启动以及 Spring Bean 异步初始化能力,用于加快应用启动速度。
本文介绍如何使用 SOFABoot 异步初始化 Spring Bean 能力以提高应用启动速度。
使用场景
在实际使用 Spring/Spring Boot 开发中,一些 Bean 在初始化过程中执行准备操作,如拉取远程配置、初始化数据源等等。
在应用启动期间,这些 Bean 会增加 Spring 上下文刷新时间,导致应用启动耗时变长。
为了加速应用启动,SOFABoot 通过配置可选项,将 Bean 的初始化方法(init-method)使用单独线程异步执行,加快 Spring 上下文加载过程,提高应用启动速度。
引入依赖
在工程的 pom.xml 文件中,引入如下 starter:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alipay.sofa</groupId>
<artifactId>runtime-sofa-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
使用方法
异步初始化 Bean 的原理是开启单独线程负责执行 Bean 的初始化方法(init-method)。
因此,除了引入上述依赖,还需要在 Bean 的 XML 定义中配置 async-init=“true” 属性,用于指定是否异步执行该 Bean 的初始化方法,例如:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:sofa="http://sofastack.io/schema/sofaboot"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://sofastack.io/schema/sofaboot http://sofastack.io/schema/sofaboot.xsd"
default-autowire="byName">
<!-- async init test -->
<bean id="testBean" class="com.alipay.sofa.runtime.beans.TimeWasteBean" init-method="init" async-init="true"/>
</beans>
属性配置
SOFABoot 异步初始化能力提供两个属性配置,用于指定负责异步执行 Bean 初始化方法(init-method)的线程池大小:
-
com.alipay.sofa.boot.asyncInitBeanCoreSize:线程池基本大小,默认值为 CPU 核数加一。
-
com.alipay.sofa.boot.asyncInitBeanMaxSize:线程池中允许的最大线程数大小,默认值为 CPU 核数加一。
此配置可以通过 VM -D 参数或者 Spring Boot 配置文件 application.yml 设置。
SOFABoot Profile
Spring 框架从 3.1.X 版本开始提供了 profile 功能:
Bean Definition Profiles,SOFABoot 支持模块级 profile 能力,即在各个模块启动的时候决定模块是否能够启动。
使用 Module-Profile 激活 module
使用 SOFABoot 的 profile 功能,需要在 application.properties 文件增加 com.alipay.sofa.boot.active-profiles 字段,该字段的值为逗号分隔的字符串,表示允许激活的 profile 列表,指定该字段后,SOFABoot 会为每个可以激活的模块指定此字段表示的 profile 列表。
SOFABoot 模块的 sofa-module.properties 文件支持 Module-Profile 字段,该字段的值为逗号分隔的字符串,表示当前模块允许在哪些 profile 激活。Module-Profile 支持取反操作,
!dev 表示 com.alipay.sofa.boot.active-profiles 不包含 dev 时被激活。
当应用未指定 com.alipay.sofa.boot.active-profiles 参数时,表示应用所有模块均可启动。
SOFABoot 模块未指定 Module-Profile 时,表示当前 SOFABoot 模块可以在任何 profile 启动。
激活 dev SOFABoot 模块
application.properties 中增加配置如下:
com.alipay.sofa.boot.active-profiles=dev
该配置表示激活 profile 为 dev 的模块。
在每个需要限定为 dev profile 被激活模块的 sofa-module.properties 文件中增加如下配置:
Module-Profile=dev
配置多个激活 profile
application.properties 中增加配置如下:
com.alipay.sofa.boot.active-profiles=dev,test
该配置表示激活 profile 为 dev 或者 test 的模块。
在 SOFABoot 模块的 sofa-module.properties 文件中增加如下配置:
Module-Profile=test,product
该配置表示当 com.alipay.sofa.boot.active-profiles 包含 test 或者 product 时激活模块,由于当前指定的 com.alipay.sofa.boot.active-profiles 为 dev,test ,此模块将被激活。
Module-Profile 取反
application.properties 中增加配置如下:
com.alipay.sofa.boot.active-profiles=dev
该配置表示激活 profile 为 dev 的模块。
在 SOFABoot 模块的 sofa-module.properties 文件中增加如下配置:
Module-Profile=!product
该配置表示当 com.alipay.sofa.boot.active-profiles 不包含 product 时激活模块,由于当前指定的 com.alipay.sofa.boot.active-profiles 为 dev ,此模块将被激活。
设置激活模块 Spring 上下文的 spring.profiles.active 属性
application.properties 中增加配置如下:
com.alipay.sofa.boot.active-profiles=dev,test
该配置表示激活 profile 为 dev 或者 test 的模块,当一个模块满足上面的激活条件时,这个模块就会被启动,同时 Spring 上下文的环境信息 spring.profiles.active 也被设置为了 dev,test ,这样如下的配置 beanId 为 devBeanId 和 testBeanId 的bean都会被激活。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"
default-autowire="byName">
<beans profile="dev">
<bean id="devBeanId" class="com.alipay.cloudenginetest.sofaprofilesenv.DemoBean">
<property name="name">
<value>demoBeanDev</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
<beans profile="test">
<bean id="testBeanId" class="com.alipay.cloudenginetest.sofaprofilesenv.DemoBean">
<property name="name">
<value>demoBeanTest</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
</beans>
SOFABoot 拓展点
SOFABoot 支持模块化隔离,在实际的使用场景中,一个模块中的 bean 有时候需要开放一些入口,供另外一个模块扩展。
SOFABoot 借鉴和使用了 Nuxeo Runtime 项目 以及 nuxeo 项目,并在上面扩展,与 Spring 融合,提供扩展点的能力。
使用
在 SOFABoot 中使用扩展点能力,需要以下三个步骤:
定义提供扩展能力的 bean
在使用 SOFABoot 扩展点能力时,首先需要定一个需要被扩展的 bean,先定一个接口:
package com.alipay.sofa.boot.test;
public interface IExtension {
String say();
}
定义这个接口的实现:
package com.alipay.sofa.boot.test.impl;
public class ExtensionImpl implements IExtension {
private String word;
@Override
public String say() {
return word;
}
public void setWord(String word) {
this.word = word;
}
public void registerExtension(Extension extension) throws Exception {
Object[] contributions = extension.getContributions();
String extensionPoint = extension.getExtensionPoint();
if (contributions == null) {
return;
}
for (Object contribution : contributions) {
if ("word".equals(extensionPoint)) {
setWord(((ExtensionDescriptor) contribution).getValue());
}
}
}
}
在这里可以看到有一个方法:registerExtension ,暂时可以先不用管这个方法,后续会介绍其具体的作用。
在模块的 Spring 配置文件中,我们把这个 bean 给配置起来:
<bean id="extension" class="com.alipay.sofa.boot.test.impl.ExtensionImpl">
<property name="word" value="Hello, world"/>
</bean>
定义扩展点
在上面的 bean 中有一个字段 word ,在实际中,我们希望这个字段能够被其他的模块自定义进行覆盖,这里我们将其以扩展点的形式暴露出来。
首先需要一个类去描述这个扩展点:
@XObject("word")W
public class ExtensionDescriptor {
@XNode("value")
private String value;
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
}
然后在 xml 中定义扩展点:
<sofa:extension-point name="word" ref="extension">
<sofa:object class="com.alipay.sofa.boot.test.extension.ExtensionDescriptor"/>
</sofa:extension-point>
其中: - name 为扩展点的名字 - ref 为扩展点所作用在的 bean - object 为扩展点的贡献点具体的描述,这个描述是通过 XMap 的方式来进行的(XMap 的作用是将 Java 对象和 XML 文件进行映射,这里建议通过在网上搜索下 XMap 的文档来了解 XMap)
定义扩展
上述已经将扩展点定义好了,此时我们就可以对这个 bean 进行扩展了:
<sofa:extension bean="extension" point="word">
<sofa:content>
<word>
<value>newValue</value>
</word>
</sofa:content>
</sofa:extension>
其中: - bean 为扩展所作用在的 bean - point 为扩展点的名字 - content 里面的内容为扩展的定义,其会通过 XMap 将内容解析为:扩展点的贡献点具体的描述对象,在这里即为 com.alipay.sofa.boot.test.extension.ExtensionDescriptor 对象
到这里,我们可以回头看一开始在 com.alipay.sofa.boot.test.impl.ExtensionImpl 中定义的 registerExtension 方法了,SOFABoot 在解析到贡献点时,会调用被扩展 bean 的 registerExtension 方法,其中包含了用户定义的贡献点处理逻辑,在上述的例子中,获取用户定义的 value 值,并将其设置到 word 字段中覆盖 bean 中原始定义的值。
此时,调用 extension bean 的 say() 方法,可以看到返回扩展中定义的值: newValue 。
XMap 支持和扩展
上述的例子中只是一个很简单的扩展,其实 XMap 包含了非常丰富的描述能力,包括 List, Map 等,这些可以通过查看 XMap 的文档来了解。
在 SOFABoot 中,除了 XMap 原生的支持以外,还扩展了跟 Spring 集成的能力: - 通过 XNode 扩展出了 XNodeSpring - 通过 XNodeList 扩展出了 XNodeListSpring - 通过 XNodeMap 扩展出了 XNodeMapSpring
这部分的扩展能力,让扩展点的能力更加丰富,描述对象中可以直接指向一个 SpringBean(用户配置 bean 的名字,SOFABoot 会根据名字从 spring 上下文中获取到 bean),这里举一个使用 XNodeListSpring 的例子,依然是上述描述的三个步骤:
定义提供扩展能力的 bean
接口定义:
在这个接口里,返回一个 list,目标是这个 list 能够被通过扩展的方式填充
package com.alipay.sofa.boot.test;
public interface IExtension {
List<SimpleSpringListBean> getSimpleSpringListBeans();
}
其中 SimpleSpringListBean 可根据需求来定义,这里我们假设定义了一个空实现
实现:
public class IExtensionImpl implements IExtension {
private List<SimpleSpringListBean> simpleSpringListBeans = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public List<SimpleSpringListBean> getSimpleSpringListBeans() {
return simpleSpringListBeans;
}
public void registerExtension(Extension extension) throws Exception {
Object[] contributions = extension.getContributions();
String extensionPoint = extension.getExtensionPoint();
if (contributions == null) {
return;
}
for (Object contribution : contributions) {
if ("testSpringList".equals(extensionPoint)) {
simpleSpringListBeans.addAll(((SpringListExtensionDescriptor) contribution)
.getValues());
}
}
}
}
可以看到:在 registerExtension 中将通过贡献点定义的 bean 加入到 list 中,以达到让用户扩展这个 list 的能力。
在模块的 Spring 配置文件中,我们把这个 bean 给配置起来:
<bean id="iExtension" class="com.alipay.sofa.runtime.integration.extension.bean.IExtensionImpl"/>
定义扩展点
首先需要一个对象去描述:
@XObject("testSpringList")
public class SpringListExtensionDescriptor {
@XNodeListSpring(value = "value", componentType = SimpleSpringListBean.class, type = ArrayList.class)
private List<SimpleSpringListBean> values;
public List<SimpleSpringListBean> getValues() {
return values;
}
}
在这里用到了 @XNodeListSpring ,当在 xml 中配置相应 bean 的名字时, SOFABoot 会从 spring 上下文中获取到相应的 bean 实例
在 xml 中将这个扩展点定义出来
<sofa:extension-point name="testSpringList" ref="iExtension">
<sofa:object class="com.alipay.sofa.runtime.integration.extension.descriptor.SpringListExtensionDescriptor"/>
</sofa:extension-point>
参考资料
https://www.sofastack.tech/projects/sofa-boot/modular-development/
