服务端启动
netty 版本
不同版本的 Netty 实现可能会略有差异,此处版本为:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.17.Final</version>
</dependency>
启动代码
为了便于代码的定位,我们首先从服务端的启动开始看。
import com.github.houbb.log.integration.core.Log;
import com.github.houbb.log.integration.core.LogFactory;
import com.github.houbb.rpc.server.constant.RpcServerConst;
import com.github.houbb.rpc.server.handler.RpcServerHandler;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
/**
* rpc 服务端
* @author binbin.hou
* @since 0.0.1
*/
public class RpcServer extends Thread {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(RpcServer.class);
/**
* 端口号
*/
private final int port;
public RpcServer() {
this.port = RpcServerConst.DEFAULT_PORT;
}
public RpcServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 启动服务端
log.info("RPC 服务开始启动服务端");
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(workerGroup, bossGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new RpcServerHandler());
}
})
// 这个参数影响的是还没有被accept 取出的连接
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
// 这个参数只是过一段时间内客户端没有响应,服务端会发送一个 ack 包,以判断客户端是否还活着。
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
// 绑定端口,开始接收进来的链接
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(port).syncUninterruptibly();
log.info("RPC 服务端启动完成,监听【" + port + "】端口");
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().syncUninterruptibly();
log.info("RPC 服务端关闭完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("RPC 服务异常", e);
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
源码分析思路
我们顺着代码,把其中涉及到的几个点,进行简单的学习。
EventLoop 事件循环组(线程组)源码
EventLoopGroup 是一组 EventLoop 的抽象,Netty 为了更好的利用多核 CPU 资源,一般会有多个 EventLoop 同时工作,每个 EventLoop 维护着一个 Selector 实例。
流程图

整体结构
我们以使用到的 NioEventLoopGroup 为例子,对应的集成关系如下:
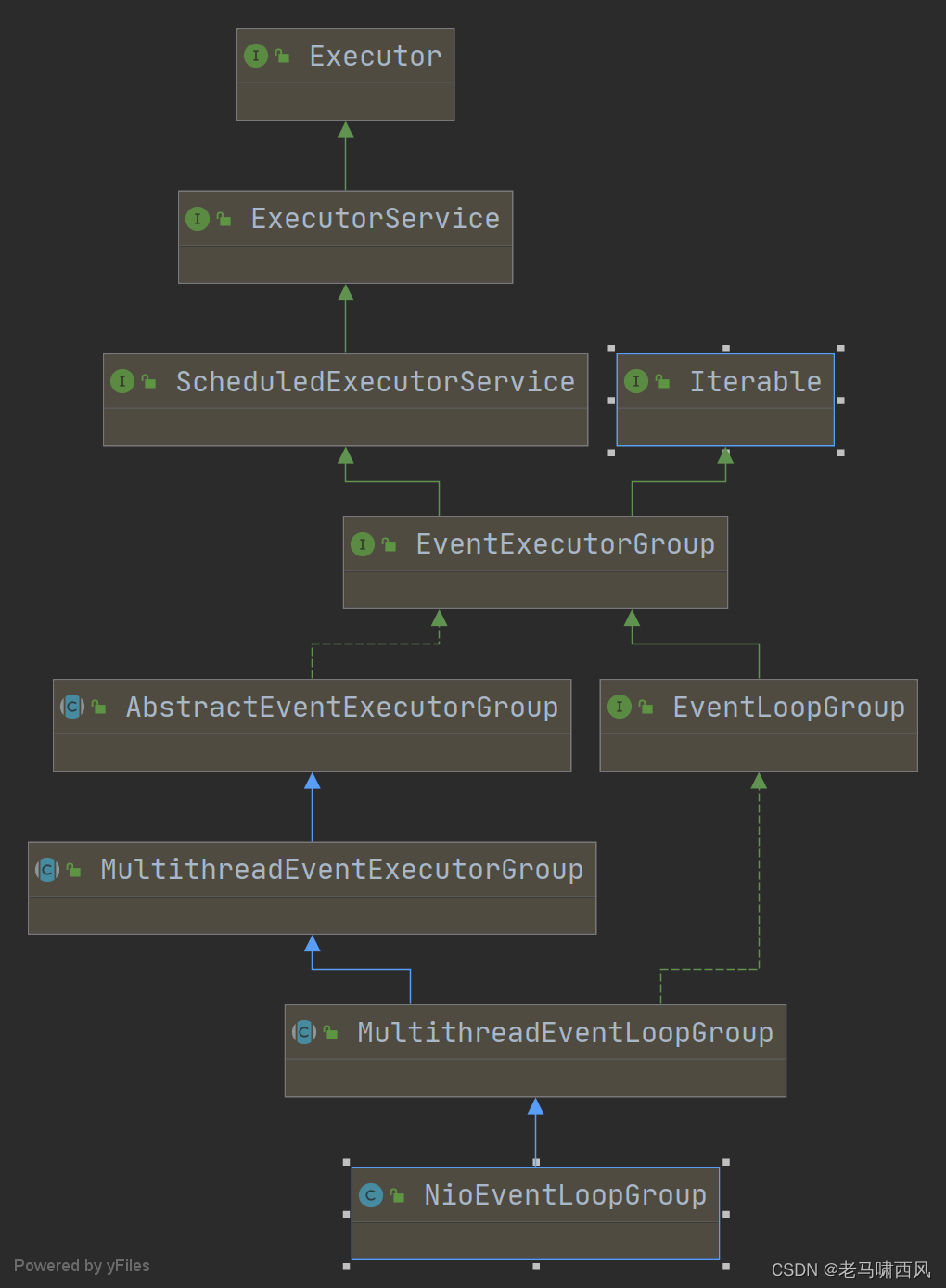
可以发现最上层就是 jdk 自带的线程池接口。
EventLoopGroup 接口
package io.netty.channel;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutorGroup;
/**
* Special {@link EventExecutorGroup} which allows registering {@link Channel}s that get processed for later selection during the event loop.
* 特殊的 {@link EventExecutorGroup} 允许注册 {@link Channel},以便在事件循环期间进行后续选择。
*/
public interface EventLoopGroup extends EventExecutorGroup {
/**
* Return the next {@link EventLoop} to use
* 返回下一个要使用的 {@link EventLoop}
*/
@Override
EventLoop next();
/**
* Register a {@link Channel} with this {@link EventLoop}. The returned {@link ChannelFuture} will get notified once the registration was complete.
* 使用此 {@link EventLoop} 注册一个 {@link Channel}。 注册完成后,返回的 {@link ChannelFuture} 将收到通知。
*/
ChannelFuture register(Channel channel);
/**
* Register a {@link Channel} with this {@link EventLoop} using a {@link ChannelFuture}.
* The passed {@link ChannelFuture} will get notified once the registration was complete and also will get returned.
* 使用 {@link ChannelFuture} 向这个 {@link EventLoop} 注册一个 {@link Channel}。
* 注册完成后,通过的 {@link ChannelFuture} 将收到通知,并且也会返回。
*/
ChannelFuture register(ChannelPromise promise);
/**
* Register a {@link Channel} with this {@link EventLoop}.
* The passed {@link ChannelFuture} will get notified once the registration was complete and also will get returned.
*
* 使用此 {@link EventLoop} 注册一个 {@link Channel}。
* 注册完成后,通过的 {@link ChannelFuture} 将收到通知,并且也会返回。
* @deprecated Use {@link #register(ChannelPromise)} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
ChannelFuture register(Channel channel, ChannelPromise promise);
}
这里面涉及几个多线程中的对象,我们稍后学习:EventLoop、ChannelFuture、Channel、ChannelPromise
我们继续看一下接口层面的抽象定义。
EventExecutorGroup 接口
其中 EventExecutorGroup 的实现如下:
其中 ScheduledExecutorService 是 jdk 中的调度实现,Iterable 也是 jdk 中的迭代器接口,此处不再赘述。
package io.netty.util.concurrent;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* The {@link EventExecutorGroup} is responsible for providing the {@link EventExecutor}'s to use via its {@link #next()} method.
* Besides this, it is also responsible for handling their life-cycle and allows shutting them down in a global fashion.
*
* {@link EventExecutorGroup} 负责通过其 {@link #next()} 方法提供 {@link EventExecutor} 以供使用。
* 除此之外,它还负责处理它们的生命周期并允许以全局方式关闭它们。
*/
public interface EventExecutorGroup extends ScheduledExecutorService, Iterable<EventExecutor> {
/**
* Returns {@code true} if and only if all {@link EventExecutor}s managed by this {@link EventExecutorGroup} are being {@linkplain #shutdownGracefully() shut down gracefully} or was {@linkplain #isShutdown() shut down}.
* 返回是否关闭
*/
boolean isShuttingDown();
/**
* Shortcut method for {@link #shutdownGracefully(long, long, TimeUnit)} with sensible default values.
*
* @return the {@link #terminationFuture()}
* shutdownGracefully 默认参数实现
*/
Future<?> shutdownGracefully();
/**
* Signals this executor that the caller wants the executor to be shut down. Once this method is called,
* {@link #isShuttingDown()} starts to return {@code true}, and the executor prepares to shut itself down.
* Unlike {@link #shutdown()}, graceful shutdown ensures that no tasks are submitted for <i>'the quiet period'</i> (usually a couple seconds) before it shuts itself down.
*
* If a task is submitted during the quiet period, it is guaranteed to be accepted and the quiet period will start over.
*
* @param quietPeriod the quiet period as described in the documentation
* @param timeout the maximum amount of time to wait until the executor is {@linkplain #shutdown()}
* regardless if a task was submitted during the quiet period
* @param unit the unit of {@code quietPeriod} and {@code timeout}
*
* @return the {@link #terminationFuture()}
* 优雅关闭,可以指定参数的实现
* 与 {@link #shutdown()} 不同,正常关闭可确保在其自行关闭之前在 <i>“静默期”</i>(通常为几秒钟)内没有提交任何任务。
* 如果在静默期提交任务,则保证被接受,静默期将重新开始。
*/
Future<?> shutdownGracefully(long quietPeriod, long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
/**
* Returns the {@link Future} which is notified when all {@link EventExecutor}s managed by this {@link EventExecutorGroup} have been terminated.
* 返回 {@link Future},当由此 {@link EventExecutorGroup} 管理的所有 {@link EventExecutor} 都已终止时,通知该 {@link Future}。
*/
Future<?> terminationFuture();
/**
* 被废弃的关闭实现
*
* @deprecated {@link #shutdownGracefully(long, long, TimeUnit)} or {@link #shutdownGracefully()} instead.
*/
@Override
@Deprecated
void shutdown();
/**
* 被废弃的立刻关闭实现
*
* @deprecated {@link #shutdownGracefully(long, long, TimeUnit)} or {@link #shutdownGracefully()} instead.
*/
@Override
@Deprecated
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
/**
* 返回下一个可以使用的 EventExecutor
*
* Returns one of the {@link EventExecutor}s managed by this {@link EventExecutorGroup}.
*/
EventExecutor next();
// 迭代器
@Override
Iterator<EventExecutor> iterator();
// 提交 Runnable 任务
@Override
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
// 提交任务
@Override
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
// 提交 Callable 任务
@Override
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
// 定时任务调度 Runnable
@Override
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit);
// 定时任务调度 Callable
@Override
<V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit);
// 固定速率调度
@Override
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit);
// 固定延迟调度
@Override
ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit);
}
这个类比较核心的方法就是 shutdownGracefully(),可以更加优雅的关闭线程池,保障任务执行完成。
也就是我们服务端在 finally 中调用的方法。
netty 对于 jdk 的重新接口定义,这里要注意下,其中的接口都被 netty 重新定义封装了:
EventExecutor、Future、ScheduledFuture。
这些都不是很难,我们逐个看一下即可。
EventExecutor 接口
EventExecutor 这个类直接继承了上面的类 EventExecutorGroup。
package io.netty.util.concurrent;
/**
* The {@link EventExecutor} is a special {@link EventExecutorGroup} which comes with some handy methods to see if a {@link Thread} is executed in a event loop.
* Besides this, it also extends the {@link EventExecutorGroup} to allow for a generic way to access methods.
* {@link EventExecutor} 是一个特殊的 {@link EventExecutorGroup},它带有一些方便的方法来查看 {@link Thread} 是否在事件循环中执行。
* 除此之外,它还扩展了 {@link EventExecutorGroup} 以允许以通用方式访问方法。
*/
public interface EventExecutor extends EventExecutorGroup {
/**
* Returns a reference to itself.
* 返回自身的引用
*/
@Override
EventExecutor next();
/**
* Return the {@link EventExecutorGroup} which is the parent of this {@link EventExecutor},
*
* 返回当前执行器的父类
*/
EventExecutorGroup parent();
/**
* Calls {@link #inEventLoop(Thread)} with {@link Thread#currentThread()} as argument
*
* 使用当前线程作为参数,调用 inEventLoop 方法
*/
boolean inEventLoop();
/**
* Return {@code true} if the given {@link Thread} is executed in the event loop, {@code false} otherwise.
* 如果给定的 {@link Thread} 在事件循环中执行,则返回 {@code true},否则返回 {@code false}。
*/
boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread);
/**
* Return a new {@link Promise}.
* 返回一个新的 {@link Promise}。
*/
<V> Promise<V> newPromise();
/**
* Create a new {@link ProgressivePromise}.
* 创建一个新的 {@link Progressive Promise}。
*/
<V> ProgressivePromise<V> newProgressivePromise();
/**
* Create a new {@link Future} which is marked as succeeded already.
* So {@link Future#isSuccess()} will return {@code true}.
* All {@link FutureListener} added to it will be notified directly.
* Also every call of blocking methods will just return without blocking.
* 创建一个已标记为已成功的新 {@link Future}。
* 所以 {@link Future#isSuccess()} 将返回 {@code true}。
* 所有添加到其中的 {@link FutureListener} 都会直接收到通知。
* 此外,阻塞方法的每次调用都会返回而不会阻塞。
*/
<V> Future<V> newSucceededFuture(V result);
/**
* Create a new {@link Future} which is marked as failed already.
* So {@link Future#isSuccess()} will return {@code false}.
* All {@link FutureListener} added to it will be notified directly.
* Also every call of blocking methods will just return without blocking.
*
* 创建一个已标记为失败的新 {@link Future}。
* 所以 {@link Future#isSuccess()} 将返回 {@code false}。
* 所有添加到其中的 {@link FutureListener} 都会直接收到通知。
* 此外,阻塞方法的每次调用都会返回而不会阻塞。
*/
<V> Future<V> newFailedFuture(Throwable cause);
}
这个接口对 EventExecutorGroup 进行了相关的拓展,其中 Promise、ProgressivePromise 都是被 netty 重新封装的。
看完了接口定义,我们来看一下对应的 NioEventLoopGroup 实现。
NioEventLoopGroup 实现
源码
/**
* {@link MultithreadEventLoopGroup} implementations which is used for NIO {@link Selector} based {@link Channel}s.
* {@link MultithreadEventLoopGroup} 实现,用于基于 NIO {@link Selector} 的 {@link Channel}。
*/
public class NioEventLoopGroup extends MultithreadEventLoopGroup {
// 各种参数的构造器
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads,
Executor executor,
EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory,
final SelectorProvider selectorProvider,
final SelectStrategyFactory selectStrategyFactory,
final RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedExecutionHandler) {
super(nThreads, executor, chooserFactory, selectorProvider, selectStrategyFactory, rejectedExecutionHandler);
}
/**
* Sets the percentage of the desired amount of time spent for I/O in the child event loops.
* The default value is {@code 50}, which means the event loop will try to spend the same amount of time for I/O as for non-I/O tasks.
* 设置子事件循环中用于 I/O 所需时间量的百分比。
* 默认值为 {@code 50},这意味着事件循环将尝试在 I/O 上花费与非 I/O 任务相同的时间。
*/
public void setIoRatio(int ioRatio) {
for (EventExecutor e: this) {
((NioEventLoop) e).setIoRatio(ioRatio);
}
}
/**
* Replaces the current {@link Selector}s of the child event loops with newly created {@link Selector}s to work around the infamous epoll 100% CPU bug.
* 用新创建的 {@link Selector} 替换子事件循环的当前 {@link Selector} 以解决臭名昭著的 epoll 100% CPU 错误。
*/
public void rebuildSelectors() {
for (EventExecutor e: this) {
((NioEventLoop) e).rebuildSelector();
}
}
@Override
protected EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception {
return new NioEventLoop(this, executor, (SelectorProvider) args[0],
((SelectStrategyFactory) args[1]).newSelectStrategy(), (RejectedExecutionHandler) args[2]);
}
}
这里看到 netty 是如何解决 epoll 100% CPU 问题的。
构造器
默认的构造器:
public NioEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this(nThreads, threadFactory, SelectorProvider.provider());
}
selector 的实现如下:
/**
* Returns the system-wide default selector provider for this invocation of
* the Java virtual machine.
*
* <p> The first invocation of this method locates the default provider
* object as follows: </p>
*
* <ol>
*
* <li><p> If the system property
* <tt>java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider</tt> is defined then it is
* taken to be the fully-qualified name of a concrete provider class.
* The class is loaded and instantiated; if this process fails then an
* unspecified error is thrown. </p></li>
*
* <li><p> If a provider class has been installed in a jar file that is
* visible to the system class loader, and that jar file contains a
* provider-configuration file named
* <tt>java.nio.channels.spi.SelectorProvider</tt> in the resource
* directory <tt>META-INF/services</tt>, then the first class name
* specified in that file is taken. The class is loaded and
* instantiated; if this process fails then an unspecified error is
* thrown. </p></li>
*
* <li><p> Finally, if no provider has been specified by any of the above
* means then the system-default provider class is instantiated and the
* result is returned. </p></li>
*
* </ol>
*
* <p> Subsequent invocations of this method return the provider that was
* returned by the first invocation. </p>
*
* @return The system-wide default selector provider
*/
public static SelectorProvider provider() {
// 同步加锁
synchronized (lock) {
if (provider != null)
return provider;
return AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<SelectorProvider>() {
public SelectorProvider run() {
if (loadProviderFromProperty())
return provider;
if (loadProviderAsService())
return provider;
provider = sun.nio.ch.DefaultSelectorProvider.create();
return provider;
}
});
}
}
MultithreadEventLoopGroup 实现
线程数的获取
public abstract class MultithreadEventLoopGroup extends MultithreadEventExecutorGroup implements EventLoopGroup {
private static final int DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS;
static {
DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt(
"io.netty.eventLoopThreads", NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2));
// log
}
}
可以发现,默认值是 NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2, 即 cpu 的核数的2倍。
构造器
指定参数的构造器,整体比较简单。
// 省略
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory,
Object... args) {
super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, chooserFactory, args);
}
其他方法
其他方法如下:
// 最大优先级
@Override
protected ThreadFactory newDefaultThreadFactory() {
return new DefaultThreadFactory(getClass(), Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
}
@Override
public EventLoop next() {
return (EventLoop) super.next();
}
@Override
protected abstract EventLoop newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception;
// 注册一个 channel
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return next().register(channel);
}
// 注册一个 ChannelPromise
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(ChannelPromise promise) {
return next().register(promise);
}
@Deprecated
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel, ChannelPromise promise) {
return next().register(channel, promise);
}
MultithreadEventExecutorGroup 源码
属性
/**
* {@link EventExecutorGroup} 实现的抽象基类,它同时使用多个线程处理它们的任务。
*/
public abstract class MultithreadEventExecutorGroup extends AbstractEventExecutorGroup {
// 子节点数组
private final EventExecutor[] children;
// 只读子节点
private final Set<EventExecutor> readonlyChildren;
// 计数器
private final AtomicInteger terminatedChildren = new AtomicInteger();
// Promise 策略
private final Promise<?> terminationFuture = new DefaultPromise(GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE);
// 选择器
private final EventExecutorChooserFactory.EventExecutorChooser chooser;
//...
}
构造器
只看最核心的一个:
/**
* Create a new instance.
*
* @param nThreads the number of threads that will be used by this instance.
* @param executor the Executor to use, or {@code null} if the default should be used.
* @param chooserFactory the {@link EventExecutorChooserFactory} to use.
* @param args arguments which will passed to each {@link #newChild(Executor, Object...)} call
*/
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor,
EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory, Object... args) {
// 基本的校验
if (nThreads <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("nThreads: %d (expected: > 0)", nThreads));
}
if (executor == null) {
executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());
}
// 循环构建
children = new EventExecutor[nThreads];
for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i ++) {
boolean success = false;
try {
children[i] = newChild(executor, args);
success = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: Think about if this is a good exception type
throw new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e);
} finally {
// 如果构建失败,则进行优雅关闭
if (!success) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
children[j].shutdownGracefully();
}
for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {
EventExecutor e = children[j];
try {
while (!e.isTerminated()) {
e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
} catch (InterruptedException interrupted) {
// Let the caller handle the interruption.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
}
}
}
// 添加选择器对应的 Listener
chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(children);
final FutureListener<Object> terminationListener = new FutureListener<Object>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Object> future) throws Exception {
if (terminatedChildren.incrementAndGet() == children.length) {
terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);
}
}
};
for (EventExecutor e: children) {
e.terminationFuture().addListener(terminationListener);
}
// 初始化 readonlyChildren
Set<EventExecutor> childrenSet = new LinkedHashSet<EventExecutor>(children.length);
Collections.addAll(childrenSet, children);
readonlyChildren = Collections.unmodifiableSet(childrenSet);
}
这里的核数,默认就是 cpu 的核数的 2 倍。
方法
因为存在多个 children 节点,所以对应的实现也要处理多个。
比如优雅关闭:
@Override
public Future<?> shutdownGracefully(long quietPeriod, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
for (EventExecutor l: children) {
l.shutdownGracefully(quietPeriod, timeout, unit);
}
return terminationFuture();
}
terminationFuture 实现如下:
@Override
public Future<?> terminationFuture() {
return terminationFuture;
}
其他的几个 shutdown 等方法也是循环处理:
// 有一个未满足,则为假
@Override
public boolean isShuttingDown() {
for (EventExecutor l: children) {
if (!l.isShuttingDown()) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 有一个未满足,则为假
@Override
public boolean isShutdown() {
for (EventExecutor l: children) {
if (!l.isShutdown()) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// 有一个未满足,则为假
@Override
public boolean isTerminated() {
for (EventExecutor l: children) {
if (!l.isTerminated()) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
long deadline = System.nanoTime() + unit.toNanos(timeout);
loop: for (EventExecutor l: children) {
for (;;) {
long timeLeft = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (timeLeft <= 0) {
break loop;
}
if (l.awaitTermination(timeLeft, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS)) {
break;
}
}
}
return isTerminated();
}
next() 方法
这里将 next 方法重点说一下,因为 AbstractEventExecutorGroup 中会用到。
public EventExecutor next() {
return chooser.next();
}
其中 chooser 的初始化:
chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(children);
这里直接看一下默认的 DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory 策略即可:
@Override
public EventExecutorChooser newChooser(EventExecutor[] executors) {
if (isPowerOfTwo(executors.length)) {
return new PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser(executors);
} else {
return new GenericEventExecutorChooser(executors);
}
}
这里根据线程数是否为 2 个次幂,分成 2 种策略,默认是 2 的次幂的。
则对应的 next 实现为:
private static final class PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser implements EventExecutorChooser {
private final AtomicInteger idx = new AtomicInteger();
private final EventExecutor[] executors;
PowerOfTwoEventExecutorChooser(EventExecutor[] executors) {
this.executors = executors;
}
@Override
public EventExecutor next() {
// 通过 & 运算,说白了就是从 0 到最后遍历返回。
// 每次 idx 会增加
return executors[idx.getAndIncrement() & executors.length - 1];
}
}
AbstractEventExecutorGroup 实现
这个类整体实现比较简单,就是调用 next() 触发对应的实现。
/**
* Abstract base class for {@link EventExecutorGroup} implementations.
*/
public abstract class AbstractEventExecutorGroup implements EventExecutorGroup {
@Override
public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) {
return next().submit(task);
}
@Override
public <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result) {
return next().submit(task, result);
}
@Override
public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) {
return next().submit(task);
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
return next().schedule(command, delay, unit);
}
@Override
public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
return next().schedule(callable, delay, unit);
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit) {
return next().scheduleAtFixedRate(command, initialDelay, period, unit);
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
return next().scheduleWithFixedDelay(command, initialDelay, delay, unit);
}
@Override
public Future<?> shutdownGracefully() {
return shutdownGracefully(DEFAULT_SHUTDOWN_QUIET_PERIOD, DEFAULT_SHUTDOWN_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* @deprecated {@link #shutdownGracefully(long, long, TimeUnit)} or {@link #shutdownGracefully()} instead.
*/
@Override
@Deprecated
public abstract void shutdown();
/**
* @deprecated {@link #shutdownGracefully(long, long, TimeUnit)} or {@link #shutdownGracefully()} instead.
*/
@Override
@Deprecated
public List<Runnable> shutdownNow() {
shutdown();
return Collections.emptyList();
}
@Override
public <T> List<java.util.concurrent.Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException {
return next().invokeAll(tasks);
}
@Override
public <T> List<java.util.concurrent.Future<T>> invokeAll(
Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return next().invokeAll(tasks, timeout, unit);
}
@Override
public <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
return next().invokeAny(tasks);
}
@Override
public <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
return next().invokeAny(tasks, timeout, unit);
}
@Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
next().execute(command);
}
}
参考资料
https://www.jianshu.com/p/568f2c25f63e
https://www.jianshu.com/p/568f2c25f63e
