什么是LDAP?
(一)在介绍什么是LDAP之前,我们先来复习一个东西:“什么是目录服务?”
-
目录服务是一个特殊的数据库,用来保存描述性的、基于属性的详细信息,支持过滤功能。
-
是动态的,灵活的,易扩展的。
如:人员组织管理,电话簿,地址簿。
(二)了解完目录服务后,我们再来看看LDAP的介绍:
LDAP(Light Directory Access Portocol),它是基于X.500标准的轻量级目录访问协议。
目录是一个为查询、浏览和搜索而优化的数据库,它成树状结构组织数据,类似文件目录一样。
目录数据库和关系数据库不同,它有优异的读性能,但写性能差,并且没有事务处理、回滚等复杂功能,不适于存储修改频繁的数据。所以目录天生是用来查询的,就好象它的名字一样。
LDAP目录服务是由目录数据库和一套访问协议组成的系统。
(三)为什么要使用
LDAP是开放的Internet标准,支持跨平台的Internet协议,在业界中得到广泛认可的,并且市场上或者开源社区上的大多产品都加入了对LDAP的支持,因此对于这类系统,不需单独定制,只需要通过LDAP做简单的配置就可以与服务器做认证交互。“简单粗暴”,可以大大降低重复开发和对接的成本。
我们拿开源系统(YAPI)做案例,只需做一下简单的几步配置就可以达到LDAP的单点登录认证了:
{
"ldapLogin": {
"enable": true,
"server": "ldap://l-ldapt1.ops.dev.cn0.qunar.com",
"baseDn": "CN=Admin,CN=Users,DC=test,DC=com",
"bindPassword": "password123",
"searchDn": "OU=UserContainer,DC=test,DC=com",
"searchStandard": "mail"
}
}
应用场景
LDAP 的主要应用场景
1.网络服务:DNS服务
2.统一认证服务:
3.Linux PAM (ssh, login, cvs. . . )
4.Apache访问控制
5.各种服务登录(ftpd, php based, perl based, python based. . . )
6.个人信息类,如地址簿
7.服务器信息,如帐号管理、邮件服务等
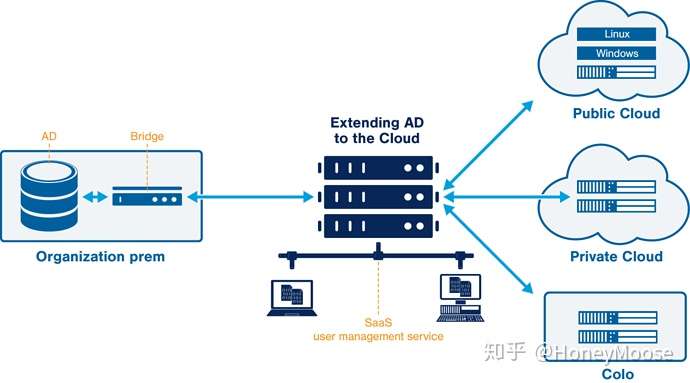
作为一般的公司来说,LDAP 很多时候被用来权限认证,软件和内部系统的用户管理和认证。
设想下,你有一个软件公司,公司里面有超过上千的员工,你们公司可能会用到各种软件,比如说 JIRA,Wiki,代码库,考勤系统等等。
LDAP 就充当了授权的这个角色,你可用在 LDAP 中对用户进行授权,分组,这样你的用户就会具有不通过软件平台的访问权限了。
现在公司的流动性也非常强,每天都会有入职的也会有离职的,对每一个人都要进行授权,撤销权限,跨域管理等等与用户有关的操作,在大一点的公司这个简直就是灾难。
LDAP 能够很好的解决这个问题。
LDAP的主要产品
细心的朋友应该会主要到,LDAP的中文全称是:轻量级目录访问协议,说到底LDAP仅仅是一个访问协议,那么我们的数据究竟存储在哪里呢?
来,我们一起看下下面的表格:
| 厂商 | 产品 | 介绍 |
|---|---|---|
| SUN | SUNONE Directory Server | 基于文本数据库的存储,速度快 |
| IBM | IBM Directory Server | 基于DB2 的的数据库,速度一般。 |
| Novell | Novell Directory Server | 基于文本数据库的存储,速度快, 不常用到。 |
| Microsoft | Microsoft Active Directory | 基于WINDOWS系统用户,对大数据量处理速度一般,但维护容易,生态圈大,管理相对简单。 |
| Opensource | Opensource | OpenLDAP 开源的项目,速度很快,但是非主 流应用。 |
LDAP的基本模型
每一个系统、协议都会有属于自己的模型,LDAP也不例外,在了解LDAP的基本模型之前我们需要先了解几个LDAP的目录树概念:
(一)目录树概念
-
目录树:在一个目录服务系统中,整个目录信息集可以表示为一个目录信息树,树中的每个节点是一个条目。
-
条目:每个条目就是一条记录,每个条目有自己的唯一可区别的名称(DN)。
-
对象类:与某个实体类型对应的一组属性,对象类是可以继承的,这样父类的必须属性也会被继承下来。
-
属性:描述条目的某个方面的信息,一个属性由一个属性类型和一个或多个属性值组成,属性有必须属性和非必须属性。
(二)DC、UID、OU、CN、SN、DN、RDN
| 关键字 | 英文全称 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| dc | Domain Component | 域名的部分,其格式是将完整的域名分成几部分,如域名为example.com变成dc=example,dc=com(一条记录的所属位置) |
| uid | User Id | 用户ID songtao.xu(一条记录的ID) |
| ou | Organization Unit | 组织单位,组织单位可以包含其他各种对象(包括其他组织单元),如“oa组”(一条记录的所属组织) |
| cn | Common Name | 公共名称,如“Thomas Johansson”(一条记录的名称) |
| sn | Surname | 姓,如“许” |
| dn | Distinguished Name | “uid=songtao.xu,ou=oa组,dc=example,dc=com”,一条记录的位置(唯一) |
| rdn | Relative dn | 相对辨别名,类似于文件系统中的相对路径,它是与目录树结构无关的部分,如“uid=tom”或“cn= Thomas Johansson” |
LDAP java 实现
java 的实现也比较简单,比如验证登录。
public void login(String username, String password) {
log.info("开始执行 {} 登录", username);
try {
Hashtable env = new Hashtable();
String ldapUrl = "ldap://xxx.xxx.xx.xx:xxx";
env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY,"com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory");
env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, ldapUrl);
env.put(Context.SECURITY_AUTHENTICATION, "simple");
env.put(Context.SECURITY_PRINCIPAL, username);
env.put(Context.SECURITY_CREDENTIALS, password);
// 初始化上下文(拥有验证功能)
InitialDirContext dc = new InitialDirContext(env);
log.info("登陆成功 {}", username);
} catch (javax.naming.AuthenticationException e) {
log.error("{} 登录验证失败", username);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("{} 登录验证异常", username);
}
}
查询功能
public String JNDILookup() {
// 连接LDAP库
Hashtable env = new Hashtable<>();
String url = "ldap://xx.xx.xx.xx:389/";
String searchBase = "OU=xx,DC=xx,DC=xx,DC=com,DC=cn";
String user = "xxx";
String password = "xxx";
env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, "com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory"); //LDAP工厂
env.put(Context.SECURITY_AUTHENTICATION, "simple"); //LDAP访问安全级别
env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, url);
env.put(Context.SECURITY_PRINCIPAL, user);
env.put(Context.SECURITY_CREDENTIALS, password);
env.put("java.naming.ldap.attributes.binary", "objectSid objectGUID");
LdapContext ctx = null;
try {
ctx = new InitialLdapContext(env, null);
// 根据条件查询
String cn = "xxx";
String filter = "(&(objectClass=top)(objectClass=organizationalPerson)(cn=" + cn + "))";
//String filter = "(&(objectClass=top)(objectClass=organizationalPerson))";
SearchControls searchControls = new SearchControls();
String[] attrNames = {"cn", "mail"};
searchControls.setSearchScope(SearchControls.SUBTREE_SCOPE);
//设置将被返回的Attribute
searchControls.setReturningAttributes(attrNames);
NamingEnumeration<SearchResult> search = ldapCtx.search(searchBase, filter.toString(), searchControls);
while (search.hasMore()) {
SearchResult result = search.next();
NamingEnumeration<? extends Attribute> attrs = result.getAttributes().getAll();
while (attrs.hasMore()) {
Attribute attr = attrs.next();
System.out.println(attr.getID() + "=====" + attr.get());
}
System.out.println("===========");
}
} catch (NamingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (ctx != null) {
try {
ctx.close();
} catch (NamingException e) {
}
}
}
return "返回信息";
}
LdapQueryBuilder类封装使用
Spring Data 提供了基于 LDAP 协议访问的 API,需要注意的是,在开发的时候需要将 LDAP 认为是一个数据库,只是与普通数据库不同的是,LDAP 使用的是 LDAP 的协议。
否则,在用户分组查询,等基于 Spring Data LDAP 的编程过程中,你可能会感到非常困惑。
在application.yml中写入LDAP相关的配置信息,通过@Value注解赋值
@Configuration
public class LdapConfig {
@Autowired
private GlobalSettings globalSettings;
@Bean
@Primary
public LdapContextSource ldapContextSource() {
LdapContextSource ldapContextSource = new LdapContextSource();
ldapContextSource.setUrl(globalSettings.getLdapUrl());
ldapContextSource.setBase(globalSettings.getLdapBase());
ldapContextSource.setUserDn(globalSettings.getLdapUser());
ldapContextSource.setPassword(globalSettings.getLdapPass());
return ldapContextSource;
}
@Bean
@Primary
// LdapTemplate:连接LDAP库
public LdapTemplate ldapTemplate() {
LdapTemplate ldapTemplate = new LdapTemplate();
ldapTemplate.setContextSource(ldapContextSource());
return ldapTemplate;
}
}
通过浏览器输入ldap中某一个用户的登录信息后获取其他信息,首先注入ldapTemplate
public HashMap<Object, Object> login(String userid, String password) {
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
try {
// 查询的用户条件
ContainerCriteria containerCriteria = LdapQueryBuilder.query()
.base(LdapUtils.emptyLdapName())
.where("objectClass").is("person")
.and("sAMAccountName").is(userid);
LdapName ldapName = ldapTemplate.authenticate(containerCriteria, password, (ctx, ldapEntryIdentification) -> ldapEntryIdentification.getRelativeName());
// 查询ldap中字段
final String[] ATTRS = {"sAMAccountName", "mail", "name"};
User lookupedUser = ldapTemplate.lookup(ldapName, ATTRS, new AbstractContextMapper<User>() {
@Override
protected User doMapFromContext(DirContextOperations ctx) {
User user = new User();
user.setUsername(ctx.getStringAttribute(ATTRS[0]));
user.setEmail(ctx.getStringAttribute(ATTRS[1]));
user.setName(ctx.getStringAttribute(ATTRS[2]));
return user;
}
});
hashMap.put("isSuccess",true);
hashMap.put("info",lookupedUser.toString());
return hashMap;
}
}
openldp
https://www.openldap.org/
参考资料
https://www.zhihu.com/question/21594237
更多学习
更多实时资讯,前沿技术,生活趣事。尽在【老马啸西风】
交流社群:[交流群信息](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/rkSvXxiiLGjl3S-ZOZCr0Q)
