一、概览
1.steal/no-force策略
lab6要实现的是simpledb的日志系统,以支持回滚和崩溃恢复;
在lab4事务中,我们并没有考虑事务执行过程中,如果机器故障或者停电了数据丢失的问题,bufferpool采用的是no-steal/force的策略,而这个实验我们实现的是steal/no-force策略,两种策略的区别如下:
-
steal/no-steal: 是否允许一个uncommitted的事务将修改更新到磁盘,如果是steal策略,那么此时磁盘上就可能包含uncommitted的数据,因此系统需要记录undo log,以防事务abort时进行回滚(roll-back)。如果是no steal策略,就表示磁盘上不会存在uncommitted数据,因此无需回滚操作,也就无需记录undo log。
-
force/no-force: force策略表示事务在committed之后必须将所有更新立刻持久化到磁盘,这样会导致磁盘发生很多小的写操作(更可能是随机写)。no-force表示事务在committed之后可以不立即持久化到磁盘, 这样可以缓存很多的更新批量持久化到磁盘,这样可以降低磁盘操作次数(提升顺序写),但是如果committed之后发生crash,那么此时已经committed的事务数据将会丢失(因为还没有持久化到磁盘),因此系统需要记录redo log,在系统重启时候进行前滚(roll-forward)操作。
2.redo log与undo log
为了支持steal/no-force策略,即我们可以将未提交事务的数据更新到磁盘,也不必在事务提交时就一定将修改的数据刷入磁盘,我们需要用日志来记录一些修改的行为。
在simpledb中,日志不区分redo log和undo log,格式较为简单,也不会记录事务执行过程中对记录的具体修改行为。
在 simpledb 中, redolog 和 undolog 是合在一起表示的, 都是 update 类型的日志.
对于redo log,为确保事务的持久性,redo log需要事务操作的变化,simpledb中用UPDATE格式的日志来保存数据的变化,在每次将数据页写入磁盘前需要用logWrite()方法来记录变化
这样,对于这些脏页,即使断电丢失数据了,我们也可以通过事务id来判断事务是否已经提交(这里提交事务会记录另一种格式的日志),如果事务已经提交,则重启时根据日志的内容就可以把数据恢复了;总而言之,通过这样的方式,可以让simpledb支持崩溃恢复;
对于undo log,我们采用的是对heappage中保存一份旧数据:
byte[] oldData;
数据页一开始的旧数据是空的,那什么时候会对旧数据进行更新呢?
答案是事务提交时,当事务提交时,就意味着这个修改已经是持久化到磁盘了,新的事务修改后就数据页的数据就是脏数据了,而在新事务回滚时,由于我们采用的是steal策略,脏页可能已经在页面淘汰时被写入磁盘中了,那么该如何进行恢复呢?
答案是before-image,即oldData,通过上一次成功事务的数据,我们可以恢复到事务开始前的样子,这样,就可以实现了事务的回滚了。
3.日志格式与checkpoint
在实验开始前应该理清楚几种日志的格式,对于后面写代码很重要,格式说明在LogFile的注释中有;
The format of the log file is as follows:
- The first long integer of the file represents the offset of the last written checkpoint, or -1 if there are no checkpoints
- All additional data in the log consists of log records. Log records are variable length.
- Each log record begins with an integer type and a long integer transaction id.
- Each log record ends with a long integer file offset representing the position in the log file where the record began.
- There are five record types: ABORT, COMMIT, UPDATE, BEGIN, and CHECKPOINT
- ABORT, COMMIT, and BEGIN records contain no additional data
- UPDATE RECORDS consist of two entries, a before image and an after image. These images are serialized Page objects, and can be
> accessed with the LogFile.readPageData() and LogFile.writePageData() methods. See LogFile.print() for an example.
- CHECKPOINT records consist of active transactions at the time the checkpoint was taken and their first log record on disk. The format of the record is an integer count of the number of transactions, as well as a long integer transaction id and a long integer first record offset for each active transaction.
简单来说,simpledb的日志记录一共有5种:ABORT, COMMIT, UPDATE, BEGIN, and CHECKPOINT,分别记录事务失败、事务提交、写入磁盘前的脏页、事务开始、检测点,这些格式的日志都记录在同一个日志文件中;日志文件以及每条日志的通用格式如下:
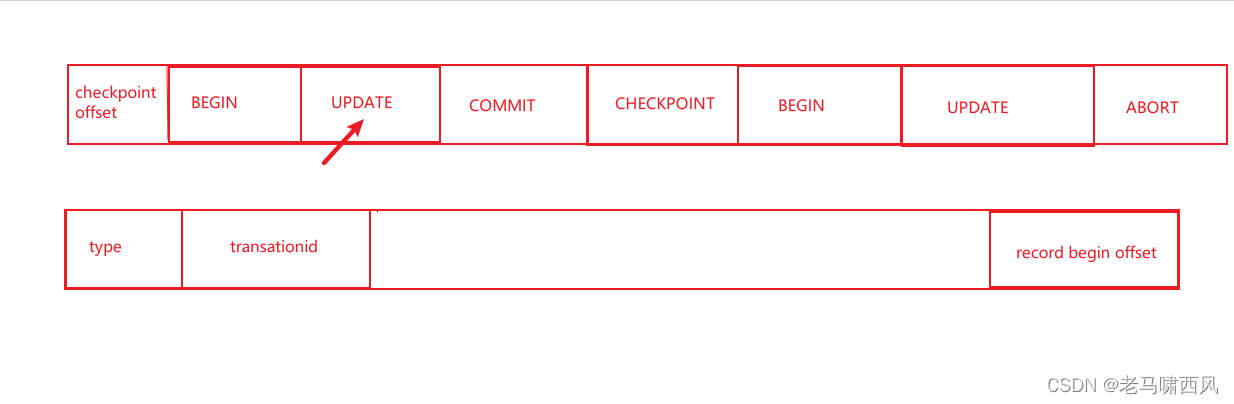
对于ABORT, COMMIT, and BEGIN这三种,中间的content是空的;对于UPDATE格式的记录,有两部分组成,即before image和after image,分别记录修改前和修改后的日志;事务提交失败回滚我们会用到before image,事务提交成功但数据由于故障丢失数据我们会用到after image;对于CHECKPOINT 记录,主要记录在checkpoint点活跃的事务数,以及每个事务的的事务id和第一条日志记录的偏移量;
其中checkpoint可以说是整个日志文件的核心,在崩溃恢复时很有用;在崩溃恢复时,我们会读取到checkpoint所在的位置,在checkpoint之前的修改已经是刷入磁盘的,除非磁盘坏了否则就是永久不会丢失的;对于checkpoint之后的日志,我们只保证修改持久化到日志,但未保证将日志记录的内容持久化到磁盘,因此崩溃恢复时,我们需要从checkpoint开始往后读,然后根据日志记录进行恢复。
二、实验过程
该实验主要分为两部分:rollback和recovery
1.Rollback
rollback是undo log做的事,即提供上一个版本的快照(相比MVCC真是微不足道),在回滚时将上一个版本的数据写回磁盘,思路比较简单:
-
根据tidToFirstLogRecord获取该事务第一条记录的位置;
-
移动到日志开始的地方;
-
根据日志格式进行读取日志记录,读到update格式的记录时根据事务id判断是否为要修改的日志,如果是,写before image
-
如果是 checkpoint 日志, 可以直接跳过
代码如下:
public void rollback(TransactionId tid) throws NoSuchElementException, IOException {
synchronized (Database.getBufferPool()) {
synchronized (this) {
preAppend();
// some code goes here
final Long firstRecordPos = this.tidToFirstLogRecord.get(tid.getId());
this.raf.seek(firstRecordPos);
final HashSet<PageId> set = new HashSet<>();
while (true) {
try {
final int type = raf.readInt();
final long transactionId = raf.readLong();
switch (type) {
case UPDATE_RECORD: {
final Page beginPage = readPageData(this.raf);
readPageData(this.raf);
final PageId pageId = beginPage.getId();
if (transactionId == tid.getId() && !set.contains(pageId)) {
set.add(pageId);
// Discard, rewrite page
Database.getBufferPool().discardPage(beginPage.getId());
Database.getCatalog().getDatabaseFile(pageId.getTableId()).writePage(beginPage);
}
break;
}
case CHECKPOINT_RECORD: {
skipCheckPointRecord();
break;
}
}
raf.readLong();
} catch (final EOFException e) {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
2.Recovery
崩溃恢复是 redo log 要做的事,在因故障数据丢失时,有部分数据是还未写入数据库的,这个时候可以利用到 redo log。
从日志文件中,我们可以获取到checkpoint所在位置,然后对checkpoint后面的日志记录进行读取并进行恢复数据。
-
对于未提交的事务:使用before-image对其进行恢复;
-
对于已提交的事务:使用after-image对其进行恢复;
具体实现代码如下:
public void recover() throws IOException {
synchronized (Database.getBufferPool()) {
synchronized (this) {
recoveryUndecided = false;
// some code goes here
this.raf.seek(0);
final long cp = raf.readLong();
if (cp > 0) {
this.raf.seek(cp);
}
final HashSet<Long> commitIds = new HashSet<>();
final HashMap<Long, List<Page>> beforePages = new HashMap<>();
final HashMap<Long, List<Page>> afterPages = new HashMap<>();
while (true) {
try {
final int type = this.raf.readInt();
final long tid = this.raf.readLong();
switch (type) {
case UPDATE_RECORD: {
final Page beforePage = readPageData(raf);
final Page afterPage = readPageData(raf);
final List<Page> beforeList = beforePages.getOrDefault(tid, new ArrayList<>());
beforeList.add(beforePage);
final List<Page> afterList = afterPages.getOrDefault(tid, new ArrayList<>());
afterList.add(afterPage);
break;
}
case COMMIT_RECORD: {
commitIds.add(tid);
break;
}
case CHECKPOINT_RECORD: {
skipCheckPointRecord();
break;
}
}
} catch (final EOFException e) {
break;
}
}
// Roll back unCommitted txn
beforePages.forEach((tid, pages) -> {
if (!commitIds.contains(tid)) {
for (final Page page : pages) {
try {
Database.getCatalog().getDatabaseFile(page.getId().getTableId()).writePage(page);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
// Write commit pages
for (final Long commitId : commitIds) {
if (afterPages.containsKey(commitId)) {
final List<Page> pages = afterPages.get(commitId);
for (final Page page : pages) {
Database.getCatalog().getDatabaseFile(page.getId().getTableId()).writePage(page);
}
}
}
}
}
}
参考资料
https://github.com/CreatorsStack/CreatorDB/blob/master/document/lab6-resolve.md
