B+树概述
B+ 树是一种树数据结构,是一个n叉树,每个节点通常有多个孩子,一颗B+树包含根节点、内部节点和叶子节点。
B+ 树通常用于数据库和操作系统的文件系统中。
B+ 树的特点是能够保持数据稳定有序,其插入与修改拥有较稳定的对数时间复杂度。
B+ 树元素自底向上插入。
特征
一个m阶的B树具有如下几个特征:
-
根结点至少有两个子女。
-
每个中间节点都至少包含
ceil(m / 2)个孩子,最多有m个孩子。 -
每一个叶子节点都包含k-1个元素,其中 m/2 <= k <= m。
-
所有的叶子结点都位于同一层。
-
每个节点中的元素从小到大排列,节点当中k-1个元素正好是k个孩子包含的元素的值域分划。
|  |
在本例中每一个父节点都出现在子节点中,是子节点最大或者最小的元素。
而下面的例子中存在如果父结点存储的为子节点最小值,那么便不需要存储第一个子节点的内容。
【例如子节点5、8—>10、15—>16、17、18意味着我父节点存10与16即可。
而同样的例子如果父节点存最大值,那么便需要存8、15、18 】
在这里,根节点中最大的元素是15,也就是整个树中最大的元素。以后无论插入多少元素要始终保持最大元素在根节点当中。
每个叶子节点都有一个指针,指向下一个数据,形成一个有序链表。
|  |
而只有叶子节点才会有data,其他都是索引。
B+树与B树的区别
-
有k个子结点的结点必然有k个关键码;
-
非叶结点仅具有索引作用,跟记录有关的信息均存放在叶结点中。
-
树的所有叶结点构成一个有序链表,可以按照关键码排序的次序遍历全部记录。
B+树的查询操作
在单元查询的时候,B+树会自定向下逐层查找,最终找到匹配的叶子节点。例如我们查找3 。
|  |
|  |
|  |
而B+树中间节点没有Data数据,所以同样大小的磁盘页可以容纳更多的节点元素。
所以数据量相同的情况下,B+树比B树更加“矮胖“,因此使用的IO查询次数更少。
由于B树的查找并不稳定(最好的情况是查询根节点,最坏查询叶子节点)。而B树每一次查找都是稳定的。
比起B树,B+树 ①IO次数更少 ②查询性能很稳定 ③范围查询更简便
B+树的插入操作
①若为空树,那么创建一个节点并将记录插入其中,此时这个叶子结点也是根结点,插入操作结束。
此处的图片中例子的介数为5 。
a)空树中插入5。
|  |
②针对叶子类型结点:根据key值找到叶子结点,向这个叶子结点插入记录。插入后,若当前结点key的个数小于等于m-1(5-1 = 4),则插入结束。否则将这个叶子结点分裂成左右两个叶子结点,左叶子结点包含前m/2个(2个)记录,右结点包含剩下的记录,将第m/2+1个(3个)记录的key进位到父结点中(父结点一定是索引类型结点),进位到父结点的key左孩子指针向左结点,右孩子指针向右结点。将当前结点的指针指向父结点,然后执行第3步。
b)依次插入8,10,15。
|  |
c)插入16
|  |
插入16后超过了关键字的个数限制,所以要进行分裂。在叶子结点分裂时,分裂出来的左结点2个记录,右边3个记录,中间第三个数成为索引结点中的key(10),分裂后当前结点指向了父结点(根结点)。结果如下图所示。
|  |
③针对索引类型结点:若当前结点key的个数小于等于m-1(4),则插入结束。否则,将这个索引类型结点分裂成两个索引结点,左索引结点包含前(m-1)/2个key(2个),右结点包含m-(m-1)/2个key(3个),将第m/2个key进位到父结点中,进位到父结点的key左孩子指向左结点,,进位到父结点的key右孩子指向右结点。将当前结点的指针指向父结点,然后重复第3步。
d)插入17
|  |
e)插入18,插入后如下图所示
|  |
当前结点的关键字个数大于5,进行分裂。分裂成两个结点,左结点2个记录,右结点3个记录,关键字16进位到父结点(索引类型)中,将当前结点的指针指向父结点。
|  |
f)插入若干数据后
|  |
g)在上图中插入7,结果如下图所示
|  |
当前结点的关键字个数超过4,需要分裂。左结点2个记录,右结点3个记录。分裂后关键字7进入到父结点中,将当前结点的指针指向父结点,结果如下图所示。
|  |
当前结点的关键字个数超过4,需要继续分裂。左结点2个关键字,右结点2个关键字,关键字16进入到父结点中,将当前结点指向父结点,结果如下图所示。
|  |
当前结点的关键字个数满足条件,插入结束。
通过上面的图, 你会发现, 如果是叶子节点分裂, 中间的 key 会被推到父节点, 同时叶节点也会保留这个 key
但是对于树内部的索引节点, 中间的 key 不会在子节点中保留
这是因为, 中间的索引节点只存储索引, 所以可以不用保留
但是叶子节点是需要存储数据的, 所以仍需要保留
B+树的删除操作
下面是一颗5阶B树的删除过程,5阶B数的结点最少2个key,最多4个key。
如果叶子结点中没有相应的key,则删除失败。否则执行下面的步骤。
①删除叶子结点中对应的key。删除后若结点的key的个数大于等于Math.ceil(m/2) – 1(>=2),删除操作结束,否则执行第2步。
a)初始状态
|  |
b)删除22,删除后结果如下图
|  |
删除后叶子结点中key的个数大于等于2,删除结束。
②若结点的key的个数小于Math.ceil(m/2) – 1(<2),且兄弟结点key有富余(大于Math.ceil(m/2)– 1)(>2),向兄弟结点借一个记录,同时用借到的key替换父结(指当前结点和兄弟结点共同的父结点)点中的key,删除结束。否则执行第3步。
c)删除15,删除后的结果如下图所示。
|  |
删除后当前结点只有一个key,不满足条件,而兄弟结点有三个key,可以从兄弟结点借一个关键字为9的记录,同时更新将父结点中的关键字由10也变为9,删除结束。
③若结点的key的个数小于Math.ceil(m/2) – 1(<2),且兄弟结点中没有富余的key(小于Math.ceil(m/2)– 1),则当前结点和兄弟结点合并成一个新的叶子结点,并删除父结点中的key,将当前结点指向父结点(必为索引结点),执行第4步(第4步以后的操作和B树就完全一样了,主要是为了更新索引结点)。
d)删除7,删除后的结果如下图所示
|  |
当前结点关键字个数小于2,(左)兄弟结点中的也没有富余的关键字(当前结点还有个右兄弟,不过选择任意一个进行分析就可以了,这里我们选择了左边的),所以当前结点和兄弟结点合并,并删除父结点中的key,当前结点指向父结点。
|  |
④若索引结点的key的个数大于等于Math.ceil(m/2) – 1(>=2),则删除操作结束。否则执行第5步。
⑤若兄弟结点有富余,父结点key下移,兄弟结点key上移,删除结束。否则执行第6步
⑥当前结点和兄弟结点及父结点下移key合并成一个新的结点。将当前结点指向父结点,重复第4步。
此时当前结点的关键字个数小于2,兄弟结点的关键字也没有富余,所以父结点中的关键字下移,和两个孩子结点合并,结果如下图所示。
|  |
注意,通过B+树的删除操作后,索引结点中存在的key,不一定在叶子结点中存在对应的记录。
一、实验概览
先来看一下 B+ 树结构:
lab5 主要是实现B+树索引,主要有查询、插入、删除等功能,查询主要根据B+树的特性去递归查找即可,插入要考虑节点的分裂(节点tuples满的时候),删除要考虑节点内元素的重新分配(当一个页面比较空,相邻页面比较满的时候),兄弟节点的合并(当相邻两个页面的元素都比较空的时候),以上就是本实验要实现的大致内容。
In this lab you will implement a B+ tree index for efficient lookups and range
scans. We supply you with all of the low-level code you will need to implement
the tree structure. You will implement searching, splitting pages,
redistributing tuples between pages, and merging pages.
(查找,分裂页,重新分配元组,合并页)
You may find it helpful to review sections 10.3–10.7 in the textbook, which
provide detailed information about the structure of B+ trees as well as
pseudocode for searches, inserts and deletes.
As described by the textbook and discussed in class, the internal nodes in B+
trees contain multiple entries, each consisting of a key value and a left and a
right child pointer. Adjacent keys share a child pointer, so internal nodes
containing *m* keys have *m*+1 child pointers. Leaf nodes can either contain
data entries or pointers to data entries in other database files. For
simplicity, we will implement a B+tree in which the leaf pages actually contain
the data entries. Adjacent leaf pages are linked together with right and left
sibling pointers, so range scans only require one initial search through the
root and internal nodes to find the first leaf page. Subsequent leaf pages are
found by following right (or left) sibling pointers.
实验前,需要理清整个B+树的结构。
B+的页面节点类型主要有四种:
1.根节点页面:一个B+树的根节点,在SimpleDB中实现为BTreeRootPtrPage.java;
2.内部节点页面:除去根节点和叶子节点外的节点,在SimpleDB中实现为BTreeInternalPage,每个BTreeInternalPage由一个一个的entry组成;
3.叶子节点页面:存储tuple的叶子节点,在SimpleDB中实现为BTreeLeafPage;
4.头部节点页面:用于记录整个B+树中的一个页面的使用情况,在SimpleDB中实现为BTreeHeaderPage。
同时,四种页面使用PageId为区分:
public final static int ROOT_PTR = 0;
public final static int INTERNAL = 1;
public final static int LEAF = 2;
public final static int HEADER = 3;
二、实验过程
1.Search
给定一个field和一个page,要从这个page往下递归找到tuple在的叶子节点。
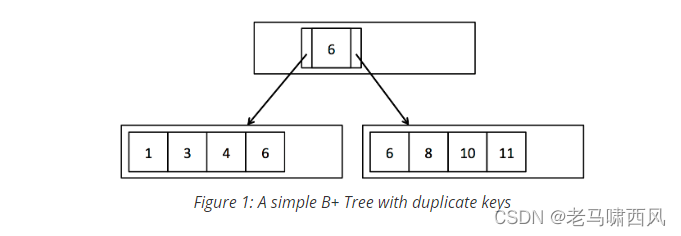
**Exercise 1: BTreeFile.findLeafPage()**
Implement `BTreeFile.findLeafPage()`.
After completing this exercise, you should be able to pass all the unit tests in `BTreeFileReadTest.java` and the system tests in `BTreeScanTest.java`.
这部分主要根据讲义的提示来做,主要实现思路如下:
-
获取数据页类型;
-
判断该数据页是否为叶子节点,如果是则递归结束,将该页面返回;
-
如果不是则说明该页面是内部节点,将页面进行类型转换;
-
获取内部节点索引的迭代器;
-
对内部节点的entry进行迭代,这里要主要field是空的处理,如果是空直接找到最左的叶子页面即可;
-
找到第一个大于(或等于)filed的entry,然后递归其左孩子;
-
如果到了最后一个页面,则递归其右孩子;
这里要对B+树的查找过程有一些概念,然后另外要注意的是读写权限的控制,根据这个权限lab4实现的事务会加不同的锁。
实现代码如下:
private BTreeLeafPage findLeafPage() {
// some code goes here
final int pageType = pid.pgcateg();
// 1.If type is leaf, search done
if (pageType == BTreePageId.LEAF) {
return (BTreeLeafPage) getPage(tid, dirtypages, pid, perm);
}
final BTreeInternalPage internalPage = (BTreeInternalPage) getPage(tid, dirtypages, pid, Permissions.READ_ONLY);
final Iterator<BTreeEntry> iterator = internalPage.iterator();
BTreeEntry entry = null;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
entry = iterator.next();
if (f == null) {
/**
* If the provided value is null, recurse on the left-most child every
* time in order to find the left-most leaf page. Finding the left-most leaf page
* is useful for scanning the entire file.
*/
return findLeafPage(tid, dirtypages, entry.getLeftChild(), perm, f);
}
if (entry.getKey().compare(Op.GREATER_THAN_OR_EQ, f)) {
return findLeafPage(tid, dirtypages, entry.getLeftChild(), perm, f);
}
}
return entry == null ? null : findLeafPage(tid, dirtypages, entry.getRightChild(), perm, f);
}
B+树索引查找的过程:
1) 创建运算符,因为该B+树只支持单列索引,运算符只有大于,小于,等于,大于等于,小于等于,不等于:
IndexPredicate ipred = new IndexPredicate(Op.GREATER_THAN, f);
2) 调用BTreeFile的indexIterator方法获取查找结果,indexIterator方法是会创建BTreeSearchIterator迭代器:
DbFileIterator it = twoLeafPageFile.indexIterator(tid, ipred);
public DbFileIterator indexIterator(TransactionId tid, IndexPredicate ipred) {
return new BTreeSearchIterator(this, tid, ipred);
}
3) 在需要获取查找结果时,会调用BTreeSearchIterator的open和getnext方法来获取查询的结果:
4) 首先是open,开启迭代器。
首先是getPage获取页面,这里会加锁,然后第一次调用会从BTreeFile.getPage()获取根节点,因为写入文件时根节点是按内部节点的类型去写的,然后每个根节点有9个entry,第一次遍历实际上是遍历了根节点的9个entry然后往下查找,当然这里只是找出了叶子节点页面并创建了迭代器,真正的查找在下一步。
public void open() throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException {
BTreeRootPtrPage rootPtr = (BTreeRootPtrPage) Database.getBufferPool().getPage(tid, BTreeRootPtrPage.getId(f.getId()), Permissions.READ_ONLY);
BTreePageId root = rootPtr.getRootId();
if(ipred.getOp() == Op.EQUALS || ipred.getOp() == Op.GREATER_THAN || ipred.getOp() == Op.GREATER_THAN_OR_EQ) {
curp = f.findLeafPage(tid, root, ipred.getField());
}
else {
curp = f.findLeafPage(tid, root, null);
}
it = curp.iterator();
}
5) 然后是要获取结果时,调用迭代器的readNext,然后会根据运算符就获取结果,这里迭代的时候是对一个leaf page的所有元组进行迭代,然后筛选出满足运算符的结果,比如说是age > 18这个条件,会先找到最后一个小于18的entry,然后获取entry的左孩子得到leaf page,然后在leaf page中迭代找到age > 18的元组,如果该leaf page 遍历完了,会一直往右兄弟的方向找下一个页面的元组,因为多个leaf page之间就是双向链表。
@Override
protected Tuple readNext() throws TransactionAbortedException, DbException, NoSuchElementException {
while (it != null) {
while (it.hasNext()) {
Tuple t = it.next();
if (t.getField(f.keyField()).compare(ipred.getOp(), ipred.getField())) {
return t;
}
else if(ipred.getOp() == Op.LESS_THAN || ipred.getOp() == Op.LESS_THAN_OR_EQ) {
// if the predicate was not satisfied and the operation is less than, we have
// hit the end
return null;
}
else if(ipred.getOp() == Op.EQUALS &&
t.getField(f.keyField()).compare(Op.GREATER_THAN, ipred.getField())) {
// if the tuple is now greater than the field passed in and the operation
// is equals, we have reached the end
return null;
}
}
BTreePageId nextp = curp.getRightSiblingId();
// if there are no more pages to the right, end the iteration
if(nextp == null) {
return null;
}
else {
curp = (BTreeLeafPage) Database.getBufferPool().getPage(tid,
nextp, Permissions.READ_ONLY);
it = curp.iterator();
}
}
}
2.Insert
In this exercise you will implement `splitLeafPage()` and `splitInternalPage()`
in `BTreeFile.java`. **If the page being split is the root page, you will need to**
**create a new internal node to become the new root page, and update the**
**BTreeRootPtrPage.** Otherwise, you will need to fetch the parent page with
**READ_WRITE permissions**, recursively split it if necessary, and **add a new entry.**
You will find the function `getParentWithEmptySlots()` extremely useful for
handling these different cases. In `splitLeafPage()` you should “copy” the key
up to the parent page, while in `splitInternalPage()` you should “push” the key
up to the parent page. See Figure 2 and review section 10.5 in the text book if
this is confusing. Remember to update the parent pointers of the new pages as
needed (for simplicity, we do not show parent pointers in the figures). When an
internal node is split, you will need to update the parent pointers of all the
children that were moved. You may find the function `updateParentPointers()`
useful for this task. Additionally, remember to update the sibling pointers of
any leaf pages that were split. **Finally, return the page into which the new**
**tuple or entry should be inserted, as indicated by the provided key field**.
(Hint: You do not need to worry about the fact that the provided key may
actually fall in the exact center of the tuples/entries to be split. You should
ignore the key during the split, and only use it to determine which of the two
pages to return.)
做完插入操作这个实验后的感觉就是,一定要仔细看讲义,讲义可以说是把大部分可能遇到的坑都先跟你说了,以及需要涉及哪些操作等。
其中getParentWithEmptySlots方法是特别有用的,帮我们考虑了如果父节点也满了会怎么样,其实就是一些情况可以特判,然后考虑递归调用spiltInternalPage来实现父节点的递归分裂,感觉这部分可以作为一个exercise自己独立完成,喂的饭太多了hhh。
**Exercise 2: Splitting Pages**
Implement `BTreeFile.splitLeafPage()` and `BTreeFile.splitInternalPage()`.
After completing this exercise, you should be able to pass the unit tests in
`BTreeFileInsertTest.java`. You should also be able to pass the system tests
in `systemtest/BTreeFileInsertTest.java`. Some of the system test cases may
take a few seconds to complete. These files will test that your code inserts
tuples and splits pages correcty, and also handles duplicate tuples.
exercise2要做的是分裂叶子节点和分裂内部节点两个方法的实现。
其实给出的图示也挺清晰的,不过到了写代码就有点难搞。
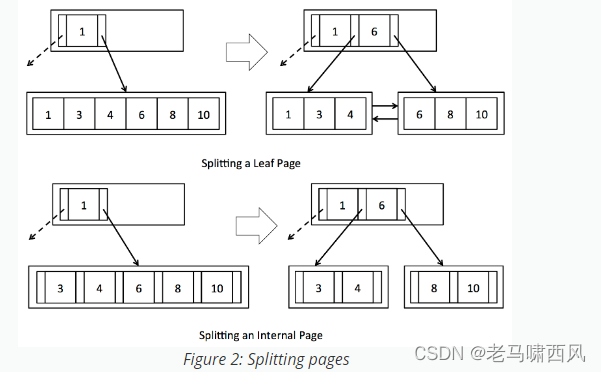
分裂叶子节点的思路:
-
新建一个leaf page,作为新的页面;
-
将满页面的元组复制到新页面,边复制边删除;
-
检查之前的满页面是否有右兄弟,有的话需要更新指针,这里有点像在双向链表中插入一个结点,一开始没有考虑到,后面测试用例过不了重新整理思路才发现要更新这个指针;
-
更新脏页;
-
更新兄弟指针;
-
找出父节点并创建entry进行插入,最后更新脏页;
-
根据field找出要插入的页面并返回;
public BTreeLeafPage splitLeafPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages, BTreeLeafPage page, Field field) {
// 1.Create a bew page
final BTreeLeafPage newPage = (BTreeLeafPage) getEmptyPage(tid, dirtypages, BTreePageId.LEAF);
int moved = page.getNumTuples() / 2;
final Iterator<Tuple> iterator = page.reverseIterator();
final List<Tuple> movedTuples = new ArrayList<>();
Tuple next = null;
while (iterator.hasNext() && moved > 0) {
moved--;
next = iterator.next();
page.deleteTuple(next);
movedTuples.add(next);
}
assert next != null : "The mid leaf entry should not be null";
for (int i = movedTuples.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
newPage.insertTuple(movedTuples.get(i));
}
// 2.Update brother page's pointer
if (page.getRightSiblingId() != null) {
final BTreePageId rigthId = page.getRightSiblingId();
final BTreeLeafPage rightPage = (BTreeLeafPage) getPage(tid, dirtypages, rigthId, Permissions.READ_ONLY);
rightPage.setLeftSiblingId(newPage.getId());
newPage.setRightSiblingId(rightPage.getId());
dirtypages.put(rightPage.getId(), rightPage);
}
// 3.Update pointer
newPage.setLeftSiblingId(page.getId());
page.setRightSiblingId(newPage.getId());
dirtypages.put(page.getId(), page);
dirtypages.put(newPage.getId(), newPage);
// 4.Update parent entry
final BTreeInternalPage parentPage = getParentWithEmptySlots(tid, dirtypages, page.getParentId(), field);
final BTreeEntry entry = new BTreeEntry(next.getField(parentPage.keyField), page.getId(), newPage.getId());
parentPage.insertEntry(entry);
dirtypages.put(parentPage.getId(), parentPage);
// 5.Update parent pointer
updateParentPointer(tid, dirtypages, parentPage.getId(), page.getId());
updateParentPointer(tid, dirtypages, parentPage.getId(), newPage.getId());
// 6.Return the page into which a tuple with the given key field should be inserted.
final boolean isRight = field.compare(Op.GREATER_THAN_OR_EQ, next.getField(parentPage.keyField));
return isRight ? newPage : page;
}
分裂内部节点的思路:
-
新建一个internal page,作为新的页面;
-
将满页面的entry复制到新页面,边复制边删除;
-
将中间节点挤出去;这里与leaf page不同,也即子节点不用保留中间节点.
-
更新脏页;
-
更新左右孩子指针;
-
更新左右叶面的孩子指针,因为前面有大量的entry插入和移除;
-
根据中间节点获取父节点,将midEntry插入到父节点中,并更新脏页和指针;
-
根据field找出要插入的页面并返回;
和分裂叶子节点, 还有一个区别是, 中间节点不是链表, 不需要更新左右兄弟指针
public BTreeInternalPage splitInternalPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages, BTreeInternalPage page,
Field field) throws DbException, IOException,
TransactionAbortedException {
// 1.move entry
final BTreeInternalPage newPage = (BTreeInternalPage) getEmptyPage(tid, dirtypages, BTreePageId.INTERNAL);
int moved = page.getNumEntries() / 2;
final Iterator<BTreeEntry> iterator = page.reverseIterator();
final List<BTreeEntry> movedTuples = new ArrayList<>();
BTreeEntry next = null;
while (iterator.hasNext() && moved > 0) {
moved--;
next = iterator.next();
page.deleteKeyAndRightChild(next);
movedTuples.add(next);
}
for (int i = movedTuples.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
newPage.insertEntry(movedTuples.get(i));
}
// 2.Get mid entry
final BTreeEntry mid = iterator.next();
page.deleteKeyAndRightChild(mid);
mid.setLeftChild(page.getId());
mid.setRightChild(newPage.getId());
// 3.Update pointer
updateParentPointers(tid, dirtypages, page);
updateParentPointers(tid, dirtypages, newPage);
dirtypages.put(page.getId(), page);
dirtypages.put(newPage.getId(), newPage);
// 4.Update parent, insert mid entry
final BTreeInternalPage parentPage = getParentWithEmptySlots(tid, dirtypages, page.getParentId(), field);
parentPage.insertEntry(mid);
dirtypages.put(parentPage.getId(), parentPage);
// 6.Return the page into which a tuple with the given key field should be inserted.
final boolean isRight = field.compare(Op.GREATER_THAN_OR_EQ, mid.getKey());
return isRight ? newPage : page;
}
3.Delete
删除的话有两种情况,一种是兄弟页面比较满,自己因为删除一些tuple或者entry比较空,这时可以从兄弟页面拿一些元素过来,这样兄弟页面可以不用那么早去分裂页面,自己也可以达到元素比较多,这个对应于exercise3要做的东西;另一种情况是两个页面都是比较空的时候,这个时候需要考虑将两个页面合并成一个,以达到节省空间的目的,这对应于exercise4要做的东西。
在前面插入的操作能够完成后,后面的套路会发现也是差不多的,然后讲义给的图示也是很容易懂的,可以帮我们理清思路。
**Exercise 3: Redistributing pages**
Implement `BTreeFile.stealFromLeafPage()`,
`BTreeFile.stealFromLeftInternalPage()`,
`BTreeFile.stealFromRightInternalPage()`.
After completing this exercise, you should be able to pass some of the unit
tests in `BTreeFileDeleteTest.java` (such as `testStealFromLeftLeafPage` and
`testStealFromRightLeafPage`). The system tests may take several seconds to
complete since they create a large B+ tree in order to fully test the system.
exercise3是页面元素的重新分配,internal page的entry,leaf page的tuple,两种页面的分配是有区别的,重新分配tuple的话parent是需要包含tuple的value的,而重新分配entry是不需要的,因为真正的数据是在leaf page中,这个只是作为一个索引,当然你加上也是没问题的,但是这样做是会更方便的,至少图示就是这样做的。
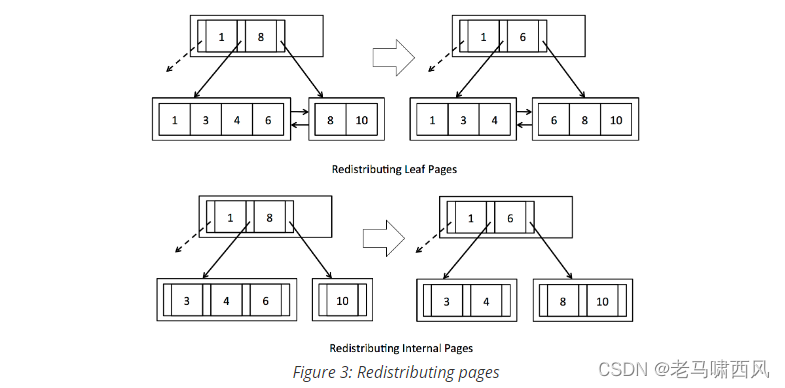
重新分配的话可以考虑两种策略:第一种是两个页面的元组总数加起来然后平均,第二种是一个页面留下总容量的1/2,剩下的都分配给比较空的页面,这里我采用的是前者;实现过程跟着图示来就好了,然后就是一些细节点注意一下就好了。
leaf page 的 steal:
public void stealFromLeafPage(BTreeLeafPage page, BTreeLeafPage sibling, BTreeInternalPage parent,
BTreeEntry entry, boolean isRightSibling) throws DbException {
// some code goes here
//
// Move some of the tuples from the sibling to the page so
// that the tuples are evenly distributed. Be sure to update
// the corresponding parent entry.
int curTuples = page.getNumTuples();
int siblingTuples = sibling.getNumTuples();
int targetTuples = curTuples + siblingTuples >> 1;
Iterator<Tuple> it = isRightSibling ? sibling.iterator() : sibling.reverseIterator();
while (it.hasNext() && curTuples < targetTuples) {
Tuple t = it.next();
sibling.deleteTuple(t);
page.insertTuple(t);
curTuples++;
}
Tuple mid = sibling.iterator().next();
entry.setKey(mid.getField(parent.keyField));
parent.updateEntry(entry);
}
internal page的steal:这里有一处坑就是前面提过的entry是挤上去的,然后steal的时候,应该最先开始更新parent的指针,这里注意一下就很好过了。
public void stealFromLeftInternalPage(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages, BTreeInternalPage page,
BTreeInternalPage leftSibling, BTreeInternalPage parent,
BTreeEntry parentEntry) throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
// Move some of the entries from the left sibling to the page so
// that the entries are evenly distributed. Be sure to update
// the corresponding parent entry. Be sure to update the parent
// pointers of all children in the entries that were moved.
int moved = leftSibling.getNumEntries() + page.getNumEntries() >> 1;
final Iterator<BTreeEntry> iterator = leftSibling.reverseIterator();
// 1.Moved parent entry to cur Page
final BTreeEntry right = iterator.next();
leftSibling.deleteKeyAndRightChild(right);
final BTreeEntry left = page.iterator().next();
final BTreeEntry entry = new BTreeEntry(parentEntry.getKey(), right.getRightChild(), left.getLeftChild());
page.insertEntry(entry);
page.insertEntry(right);
// 2.Moved entry from sibling to curPage
int curTuples = page.getNumEntries();
while (curTuples < moved && iterator.hasNext()) {
final BTreeEntry next = iterator.next();
leftSibling.deleteKeyAndRightChild(next);
page.insertEntry(next);
curTuples++;
}
// 3.Update parent entry
final BTreeEntry mid = iterator.next();
leftSibling.deleteKeyAndRightChild(mid);
parentEntry.setKey(mid.getKey());
parent.updateEntry(parentEntry);
updateParentPointers(tid, dirtypages, page);
}
做完这个就剩该实验的最后一部分的代码编写了,即实现两个页面的合并。
**Exercise 4: Merging pages**
Implement `BTreeFile.mergeLeafPages()` and `BTreeFile.mergeInternalPages()`.
Now you should be able to pass all unit tests in `BTreeFileDeleteTest.java`
and the system tests in `systemtest/BTreeFileDeleteTest.java`.
merge page 要注意的同样是指针的更新,思路还是比较清晰的,直接上代码:
public void mergeLeafPages(TransactionId tid, Map<PageId, Page> dirtypages, BTreeLeafPage leftPage,
BTreeLeafPage rightPage, BTreeInternalPage parent, BTreeEntry parentEntry){
final Iterator<Tuple> iterator = rightPage.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
final Tuple next = iterator.next();
rightPage.deleteTuple(next);
leftPage.insertTuple(next);
}
final BTreePageId rrId = rightPage.getRightSiblingId();
if (rrId != null) {
final BTreeLeafPage rr = (BTreeLeafPage) getPage(tid, dirtypages, rrId, Permissions.READ_WRITE);
rr.setLeftSiblingId(leftPage.getId());
leftPage.setRightSiblingId(rrId);
dirtypages.put(rrId, rr);
} else {
leftPage.setRightSiblingId(null);
}
dirtypages.put(leftPage.getId(), leftPage);
setEmptyPage(tid, dirtypages, rightPage.pid.getPageNumber());
deleteParentEntry(tid, dirtypages, leftPage, parent, parentEntry);
}
public void mergeInternalPages(BTreeInternalPage rightPage, BTreeInternalPage parent, BTreeEntry parentEntry) {
// Move parent key to left
BTreeEntry lastLeftEntry = leftPage.reverseIterator().next();
BTreeEntry firstRightEntry = rightPage.iterator().next();
BTreeEntry entry = new BTreeEntry(parentEntry.getKey(), lastLeftEntry.getRightChild(), firstRightEntry.getLeftChild());
leftPage.insertEntry(entry);
// move right to left
Iterator<BTreeEntry> it = rightPage.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
BTreeEntry e = it.next();
rightPage.deleteKeyAndLeftChild(e);
leftPage.insertEntry(e);
}
// update pointers
updateParentPointers(tid, dirtypages, leftPage);
setEmptyPage(tid, dirtypages, rightPage.pid.getPageNumber());
deleteParentEntry(tid, dirtypages, leftPage, parent, parentEntry);
}
三、b+树总结
search
搜索就是一个递归查询的过程
插入
插入需要考虑节点的分裂
对于叶子节点:
- 创建新的 page, 移动 oldPage 一半的数据到 newPage
- 更新兄弟指针
- 将mid tuple 的 key 插入到父节点
对于索引节点:
和叶子节点的区别在于:
- mid tuple 插入到父节点, 同时 newPage 不保存该 tuple
删除
删除需要考虑 steal 和 merge
对于 steal
steal leaf page:
- 移动数据到 rightPage
- 更新父节点的索引为 leftPage.midTuple
steal internal page:
- 先移动父节点的索引数据到 rightPage
- 数据 leftPage 数据到 rightPage
- 将 leftPage.mid 移动到父节点
对于 Merge
merge leaf page:
- 移动数据到 LeftPage
- 如果 rightPage 有右兄弟, 需要更新指针
- 删除父节点索引指针
merge internal page:
- 将父节点索引数据移到 leftPage
- 移动 rightPage 到 LeftPage
- 删除父节点索引指针
总的来说, 叶子节点需要注意兄弟指针的修改, 索引节点需要注意父节点 key 的移动.
参考资料
https://github.com/CreatorsStack/CreatorDB/blob/master/document/lab5-resolve.md
