敏感词系列
sensitive-word-admin 敏感词控台 v1.2.0 版本开源
sensitive-word-admin v1.3.0 发布 如何支持分布式部署?
05-敏感词之 DFA 算法(Trie Tree 算法)详解
06-敏感词(脏词) 如何忽略无意义的字符?达到更好的过滤效果
开源地址
为了便于大家学习,项目开源地址如下,欢迎 fork+star 鼓励一下老马~
双数组实现原理
双数组Tire树是Tire树的升级版,Tire取自英文Retrieval中的一部分,即检索树,又称作字典树或者键树。
下面简单介绍一下Tire树。
1.1 Tire树
Trie是一种高效的索引方法,它实际上是一种确定有限自动机(DFA),在树的结构中,每一个结点对应一个DFA状态,每一个从父结点指向子结点(有向)标记的边对应一个DFA转换。
遍历从根结点开始,然后从head到tail,由关键词(本想译成键字符串,感太别扭)的每个字符来决定下一个状态,标记有相同字符的边被选中做移动。
注意每次这种移动会从关键词中消耗一个字符并走向树的下一层,如果这个关键字符串空了,并且走到了叶子结点,那么我们达到了这个关键词的出口。
如果我们被困在了一点结点,比如因为没有分枝被标记为当前我们有的字符,或是因为关键字符串在中间结点就空了,这表示关键字符串没有被trie认出来。
图1.1.1即是一颗Tire树,其由字典{AC,ACE,ACFF,AD,CD,CF,ZQ}构成。
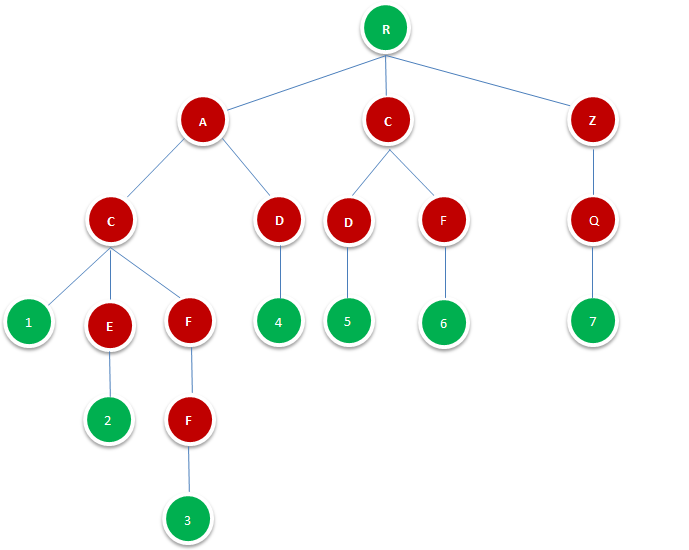
图中R表示根节点,并不代表字符,除根节点外每一个节点都只包含一个字符。
从根节点到图中绿色节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串。绿色叶节点的数字代表其在字典中的位置
说明
双数组Trie树(DoubleArrayTrie)是一种空间复杂度低的Trie树,应用于字符区间大的语言(如中文、日文等)分词领域。
双数组Trie (Double-Array Trie)结构由日本人JUN-ICHI AOE于1989年提出的,是Trie结构的压缩形式,仅用两个线性数组来表示Trie树,该结构有效结合了数字搜索树(Digital Search Tree)检索时间高效的特点和链式表示的Trie空间结构紧凑的特点。
双数组Trie的本质是一个确定有限状态自动机(DFA),每个节点代表自动机的一个状态,根据变量不同,进行状态转移,当到达结束状态或无法转移时,完成一次查询操作。
在双数组所有键中包含的字符之间的联系都是通过简单的数学加法运算表示,不仅提高了检索速度,而且省去了链式结构中使用的大量指针,节省了存储空间。
——《基于双数组 Trie 树算法的字典改进和实现》
自己的实现
接口定义
我们首先统一定义 trie-tree 的接口,和 leetcode 风格保持一致。
多一个插入列表,便于日常使用。
package com.github.houbb.trie.api;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* 前缀树接口
* @since 1.0.0
*/
public interface ITrieTree {
/**
* 插入列表
* @param words 列表
*/
void insert(Collection<String> words);
/**
* 插入单词
* @param word 单词
*/
void insert(String word);
/**
* 是否存在单词
* @param word 单词
* @return 结果
*/
boolean search(String word);
/**
* 是否以 xxx 开头
* @param prefix 开头
* @return 结果
* @since 1.0.0
*/
boolean startsWith(String prefix);
}
V1-简单版本
思路
最简单的是每一个节点,都有对应的 next 数组。
优点是实现非常简单,缺点是如果是中文、日文等体系,数组的会变得非常稀疏,直接内存爆炸。
实现
刷过 leetcode 话,这个实现自然不在话下。
我们把 arraySize 作为外部可以指定,默认为 256。
package com.github.houbb.trie.impl;
/**
* 前缀树接口
* @since 1.0.0
*/
public class TrieTreeArray extends AbstractTrieTree {
private class TrieNode {
private boolean isEnd;
private TrieNode[] next;
public TrieNode() {
this.isEnd = false;
next = new TrieNode[arraySize];
}
}
// 根节点
private TrieNode root;
/**
* 如果只是英文小写字母 26 即可,
* 如果是 ASCII,则 256
* 如果是其他的,则太大了。可能会造成数组非常的稀疏,空间的浪费。
*
* 如何优化,可以避免这种浪费呢?使用 map 替代?
*/
private int arraySize = 256;
public TrieTreeArray(int arraySize) {
this.arraySize = arraySize;
// 初始化
root = new TrieNode();
}
public TrieTreeArray() {
this(256);
}
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
int ci = getCharIndex(word.charAt(i));
if(cur.next[ci] == null) {
cur.next[ci] = new TrieNode();
}
cur = cur.next[ci];
}
// 单词结束
cur.isEnd = true;
}
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
int ci = getCharIndex(word.charAt(i));
if(cur.next[ci] == null) {
return false;
}
cur = cur.next[ci];
}
// 单词结束
return cur.isEnd;
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for(int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
int ci = getCharIndex(prefix.charAt(i));
if(cur.next[ci] == null) {
return false;
}
cur = cur.next[ci];
}
// 单词结束
return true;
}
private int getCharIndex(char c) {
return c - '\0';
}
}
V2-基于 map 实现
思路
既然直接固定长度的数组,造成了空间的浪费。我们直接使用 map 来替代好了。
实现
整体实现和上面基本类似。
package com.github.houbb.trie.impl;
import com.github.houbb.heaven.util.lang.ObjectUtil;
import com.github.houbb.heaven.util.util.MapUtil;
import com.github.houbb.trie.api.ITrieTree;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 前缀树接口
* @since 1.0.0
*/
public class TrieTreeMap extends AbstractTrieTree {
/**
* 结束标识
*/
private static final String IS_END = "ED";
/**
* 内部的 map
*/
private volatile Map map;
public TrieTreeMap() {
this.map = new HashMap();
}
@Override
public void insert(String word) {
// 用来按照相应的格式保存敏感词库数据
char[] chars = word.toCharArray();
final int size = chars.length;
// 每一个新词的循环,直接将结果设置为当前 map,所有变化都会体现在结果的 map 中
Map currentMap = map;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
// 截取敏感词当中的字,在敏感词库中字为HashMap对象的Key键值
char charKey = chars[i];
// 如果集合存在
Object wordMap = currentMap.get(charKey);
// 如果集合存在
if (ObjectUtil.isNotNull(wordMap)) {
// 直接将获取到的 map 当前当前 map 进行继续的操作
currentMap = (Map) wordMap;
} else {
//不存在则,则构建一个新的map,同时将isEnd设置为0,因为他不是最后一
Map<String, Boolean> newWordMap = new HashMap<>(8);
newWordMap.put(IS_END, false);
// 将新的节点放入当前 map 中
currentMap.put(charKey, newWordMap);
// 将新节点设置为当前节点,方便下一次节点的循环。
currentMap = newWordMap;
}
// 判断是否为最后一个,添加是否结束的标识。
if (i == size - 1) {
currentMap.put(IS_END, true);
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean search(String word) {
if(MapUtil.isEmpty(map)) {
return false;
}
// 每一个 char 都存在,且最后对应的是 ED
Map currentMap = map;
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char charKey = word.charAt(i);
Map nextMap = (Map) currentMap.get(charKey);
if(nextMap == null) {
return false;
}
currentMap = nextMap;
}
// 单词结束
return (boolean) currentMap.get(IS_END);
}
@Override
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
if(MapUtil.isEmpty(map)) {
return false;
}
// 每一个 char 都存在,且最后对应的是 ED
Map currentMap = map;
for(int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
char charKey = prefix.charAt(i);
Map nextMap = (Map) currentMap.get(charKey);
if(nextMap == null) {
return false;
}
currentMap = nextMap;
}
// 不关心是否为结尾
return true;
}
}
缺点
但是,HashMap本质上就是一个hash table;存在着一定程度上的空间浪费。
由此,容易想到用linked-list实现Trie树:虽然linked-list避免了空间浪费,却增加了查询时间复杂度,因为公共前缀就意味着多次回溯。
V3-double array 双数组实现
Double-array结合了array查询效率高、list节省空间的优点,具体是通过两个数组base、check来实现。
Trie树可以等同于一个自动机,状态为树节点的编号,边为字符;那么goto函数g(r,c)=s 则表示状态r可以按字符c转移到状态s。
base数组便是goto函数array实现,check数组为验证转移的有效性;两个数组满足如下转移方程:
base[r] + c = s
check[s] = r
值得指出的是,代入上述式子中的c为该字符的整数编码值。
为了对Trie做进一步的压缩,用tail数组存储无公共前缀的尾字符串,且满足如下的特点:
tail of string [b1..bh] has no common prefix and the corresponding state is m:
base[m] < 0;
p = -base[m], tail[p] = b1, tail[p+1] = b2, ..., tail[p+h-1] = bh;
至于如何构造数组base、check,可参考原论文 [1]及文章 [2].
我们接下来,就一起好好学习一下论文和实现文章。
TODO
…
DAT java 实现
说明
具体请参考这篇论文 An Efficient Implementation of Trie Structures,本程序的编写也是参考这篇论文的。
关于几点论文没有提及的细节和与论文不一一致的实现:
1.对于插入字符串,如果有一个字符串是另一个字符串的子串的话,我是将结束符也作为一条边,产生一个新的结点,这个结点新节点的Base我置为0
所以一个字符串结束也有2中情况:一个是Base值为负,存储剩余字符(可能只有一个结束符)到Tail数组;另一个是Base为0。
所以在查询的时候要考虑一下这两种情况
2.对于第一种冲突(论文中的Case 3),可能要将Tail中的字符串取出一部分,作为边放到索引中。论文是使用将尾串左移的方式,我的方式直接修改Base值,而不是移动尾串。
下面是java实现的代码,可以处理相同字符串插入,子串的插入等情况
java 处理
下面是java实现的代码,可以处理相同字符串插入,子串的插入等情况
/*
* Name: Double Array Trie
* Author: Yaguang Ding
* Date: 2012/5/21
* Note: a word ends may be either of these two case:
* 1. Base[cur_p] == pos ( pos<0 and Tail[-pos] == 'END_CHAR' )
* 2. Check[Base[cur_p] + Code('END_CHAR')] == cur_p
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class DoubleArrayTrie {
final char END_CHAR = '';
final int DEFAULT_LEN = 1024;
int Base[] = new int [DEFAULT_LEN];
int Check[] = new int [DEFAULT_LEN];
char Tail[] = new char [DEFAULT_LEN];
int Pos = 1;
Map<Character ,Integer> CharMap = new HashMap<Character,Integer>();
ArrayList<Character> CharList = new ArrayList<Character>();
public DoubleArrayTrie()
{
Base[1] = 1;
CharMap.put(END_CHAR,1);
CharList.add(END_CHAR);
CharList.add(END_CHAR);
for(int i=0;i<26;++i)
{
CharMap.put((char)('a'+i),CharMap.size()+1);
CharList.add((char)('a'+i));
}
}
private void Extend_Array()
{
Base = Arrays.copyOf(Base, Base.length*2);
Check = Arrays.copyOf(Check, Check.length*2);
}
private void Extend_Tail()
{
Tail = Arrays.copyOf(Tail, Tail.length*2);
}
private int GetCharCode(char c)
{
if (!CharMap.containsKey(c))
{
CharMap.put(c,CharMap.size()+1);
CharList.add(c);
}
return CharMap.get(c);
}
private int CopyToTailArray(String s,int p)
{
int _Pos = Pos;
while(s.length()-p+1 > Tail.length-Pos)
{
Extend_Tail();
}
for(int i=p; i<s.length();++i)
{
Tail[_Pos] = s.charAt(i);
_Pos++;
}
return _Pos;
}
private int x_check(Integer []set)
{
for(int i=1; ; ++i)
{
boolean flag = true;
for(int j=0;j<set.length;++j)
{
int cur_p = i+set[j];
if(cur_p>= Base.length) Extend_Array();
if(Base[cur_p]!= 0 || Check[cur_p]!= 0)
{
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag) return i;
}
}
private ArrayList<Integer> GetChildList(int p)
{
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i=1; i<=CharMap.size();++i)
{
if(Base[p]+i >= Check.length) break;
if(Check[Base[p]+i] == p)
{
ret.add(i);
}
}
return ret;
}
private boolean TailContainString(int start,String s2)
{
for(int i=0;i<s2.length();++i)
{
if(s2.charAt(i) != Tail[i+start]) return false;
}
return true;
}
private boolean TailMatchString(int start,String s2)
{
s2 += END_CHAR;
for(int i=0;i<s2.length();++i)
{
if(s2.charAt(i) != Tail[i+start]) return false;
}
return true;
}
public void Insert(String s) throws Exception
{
s += END_CHAR;
int pre_p = 1;
int cur_p;
for(int i=0; i<s.length(); ++i)
{
//获取状态位置
cur_p = Base[pre_p]+GetCharCode(s.charAt(i));
//如果长度超过现有,拓展数组
if (cur_p >= Base.length) Extend_Array();
//空闲状态
if(Base[cur_p] == 0 && Check[cur_p] == 0)
{
Base[cur_p] = -Pos;
Check[cur_p] = pre_p;
Pos = CopyToTailArray(s,i+1);
break;
}else
//已存在状态
if(Base[cur_p] > 0 && Check[cur_p] == pre_p)
{
pre_p = cur_p;
continue;
}else
//冲突 1:遇到 Base[cur_p]小于0的,即遇到一个被压缩存到Tail中的字符串
if(Base[cur_p] < 0 && Check[cur_p] == pre_p)
{
int head = -Base[cur_p];
if(s.charAt(i+1)== END_CHAR && Tail[head]==END_CHAR) //插入重复字符串
{
break;
}
//公共字母的情况,因为上一个判断已经排除了结束符,所以一定是2个都不是结束符
if (Tail[head] == s.charAt(i+1))
{
int avail_base = x_check(new Integer[]{GetCharCode(s.charAt(i+1))});
Base[cur_p] = avail_base;
Check[avail_base+GetCharCode(s.charAt(i+1))] = cur_p;
Base[avail_base+GetCharCode(s.charAt(i+1))] = -(head+1);
pre_p = cur_p;
continue;
}
else
{
//2个字母不相同的情况,可能有一个为结束符
int avail_base ;
avail_base = x_check(new Integer[]{GetCharCode(s.charAt(i+1)),GetCharCode(Tail[head])});
Base[cur_p] = avail_base;
Check[avail_base+GetCharCode(Tail[head])] = cur_p;
Check[avail_base+GetCharCode(s.charAt(i+1))] = cur_p;
//Tail 为END_FLAG 的情况
if(Tail[head] == END_CHAR)
Base[avail_base+GetCharCode(Tail[head])] = 0;
else
Base[avail_base+GetCharCode(Tail[head])] = -(head+1);
if(s.charAt(i+1) == END_CHAR)
Base[avail_base+GetCharCode(s.charAt(i+1))] = 0;
else
Base[avail_base+GetCharCode(s.charAt(i+1))] = -Pos;
Pos = CopyToTailArray(s,i+2);
break;
}
}else
//冲突2:当前结点已经被占用,需要调整pre的base
if(Check[cur_p] != pre_p)
{
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = GetChildList(pre_p);
int toBeAdjust;
ArrayList<Integer> list = null;
if(true)
{
toBeAdjust = pre_p;
list = list1;
}
int origin_base = Base[toBeAdjust];
list.add(GetCharCode(s.charAt(i)));
int avail_base = x_check((Integer[])list.toArray(new Integer[list.size()]));
list.remove(list.size()-1);
Base[toBeAdjust] = avail_base;
for(int j=0; j<list.size(); ++j)
{
//BUG
int tmp1 = origin_base + list.get(j);
int tmp2 = avail_base + list.get(j);
Base[tmp2] = Base[tmp1];
Check[tmp2] = Check[tmp1];
//有后续
if(Base[tmp1] > 0)
{
ArrayList<Integer> subsequence = GetChildList(tmp1);
for(int k=0; k<subsequence.size(); ++k)
{
Check[Base[tmp1]+subsequence.get(k)] = tmp2;
}
}
Base[tmp1] = 0;
Check[tmp1] = 0;
}
//更新新的cur_p
cur_p = Base[pre_p]+GetCharCode(s.charAt(i));
if(s.charAt(i) == END_CHAR)
Base[cur_p] = 0;
else
Base[cur_p] = -Pos;
Check[cur_p] = pre_p;
Pos = CopyToTailArray(s,i+1);
break;
}
}
}
public boolean Exists(String word)
{
int pre_p = 1;
int cur_p = 0;
for(int i=0;i<word.length();++i)
{
cur_p = Base[pre_p]+GetCharCode(word.charAt(i));
if(Check[cur_p] != pre_p) return false;
if(Base[cur_p] < 0)
{
if(TailMatchString(-Base[cur_p],word.substring(i+1)))
return true;
return false;
}
pre_p = cur_p;
}
if(Check[Base[cur_p]+GetCharCode(END_CHAR)] == cur_p)
return true;
return false;
}
//内部函数,返回匹配单词的最靠后的Base index,
class FindStruct
{
int p;
String prefix="";
}
private FindStruct Find(String word)
{
int pre_p = 1;
int cur_p = 0;
FindStruct fs = new FindStruct();
for(int i=0;i<word.length();++i)
{
// BUG
fs.prefix += word.charAt(i);
cur_p = Base[pre_p]+GetCharCode(word.charAt(i));
if(Check[cur_p] != pre_p)
{
fs.p = -1;
return fs;
}
if(Base[cur_p] < 0)
{
if(TailContainString(-Base[cur_p],word.substring(i+1)))
{
fs.p = cur_p;
return fs;
}
fs.p = -1;
return fs;
}
pre_p = cur_p;
}
fs.p = cur_p;
return fs;
}
public ArrayList<String> GetAllChildWord(int index)
{
ArrayList<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
if(Base[index] == 0)
{
result.add("");
return result;
}
if(Base[index] < 0)
{
String r="";
for(int i=-Base[index];Tail[i]!=END_CHAR;++i)
{
r+= Tail[i];
}
result.add(r);
return result;
}
for(int i=1;i<=CharMap.size();++i)
{
if(Check[Base[index]+i] == index)
{
for(String s:GetAllChildWord(Base[index]+i))
{
result.add(CharList.get(i)+s);
}
//result.addAll(GetAllChildWord(Base[index]+i));
}
}
return result;
}
public ArrayList<String> FindAllWords(String word)
{
ArrayList<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
String prefix = "";
FindStruct fs = Find(word);
int p = fs.p;
if (p == -1) return result;
if(Base[p]<0)
{
String r="";
for(int i=-Base[p];Tail[i]!=END_CHAR;++i)
{
r+= Tail[i];
}
result.add(fs.prefix+r);
return result;
}
if(Base[p] > 0)
{
ArrayList<String> r = GetAllChildWord(p);
for(int i=0;i<r.size();++i)
{
r.set(i, fs.prefix+r.get(i));
}
return r;
}
return result;
}
}
测试
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.xml.crypto.Data;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ArrayList<String> words = new ArrayList<String>();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("words3.dic")));
String s;
int num = 0;
while((s=reader.readLine()) != null)
{
words.add(s);
num ++;
}
DoubleArrayTrie dat = new DoubleArrayTrie();
for(String word: words)
{
dat.Insert(word);
}
System.out.println(dat.Base.length);
System.out.println(dat.Tail.length);
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext())
{
String word = sc.next();
System.out.println(dat.Exists(word));
System.out.println(dat.FindAllWords(word));
}
}
}
开源项目-darts-java
ps: 原项目是日文,这里简单的翻译一下。
简介
Taku Kudo 的双数组 Trie C++ 实现 (1) 已被 MURAWAKI Yugo (2) 移植到 Java。这是 Darts 的 Java 实现,具有更像 Java 的接口和改进的性能。。
(1) Darts http://www.chasen.org/~taku/software/darts/
(2) http://nlp.ist.i.kyoto-u.ac.jp/member/murawaki/misc/index.html
原始实现的改进(Java 移植版本)
-
改进的界面
-
对字符串的 char[] 表示和大量使用数组进行了修改,以创建更易于使用的类似于 Java 的界面。
-
处理输入数据导致错误的情况
-
改善堆消耗
-
减少了 Trie 构造期间和之后的堆消耗(原始实现的堆消耗约为 26%)。
-
提高执行速度
-
trie 构建(快约 2.6 倍)、精确匹配搜索(快约 1.7 倍)和公共前缀搜索(快约 1.2 倍)的处理性能得到改进。
用法
请单独使用 DoubleArrayTrie.java(用这个文件完成实现)。
基准
测试数据
Ubuntu 12 的 /usr/share/dict/words (916 KB, 99171 words) 作为测试数据。
测量方法
-
堆消耗
-
调用DoubleArrayTrie#build()前后分别通过Runtime#totalMemory() / Runtime#freeMemory()测量堆消耗,取差值计算构建后的堆消耗。
-
从文件中读取的测试数据经过build()处理50次,计算出平均值和标准差。
-
exactMatchSearch() 处理时间
-
对于基于测试数据构建的trie,对测试数据中的所有词按顺序进行精确匹配搜索的过程进行了50次,并计算了平均值和标准差。
-
commonPrefixSearch() 处理时间
-
与 exactMatchSearch() 类似,对测试数据构建的 Trie 搜索公共前缀 50 次,对测试数据中的所有词条进行排序,并计算平均值和标准差。
-
在最初的实现中,接口接收 commonPrefixSearch() 的结果作为传递给相同方法的 int 数组。调用 commonPrefixSearch()。
測定結果
original imploved
====================================================
ヒープ消費量 [byte] 62,287,864 16,780,160
----------------------------------------------------
build() [msec] 165.68 64.26
(標準偏差) (82.87) (6.74)
----------------------------------------------------
exactMatchSearch() [msec] 10.88 6.24
(標準偏差) (7.21) (7.73)
----------------------------------------------------
commonPrefixSearch() [msec] 17.18 14.04
(標準偏差) (4.68) (4.75)
----------------------------------------------------
测试
实际上官方没有给出具体的使用例子。
我们把这个类封装一下。
实现
只有一个文件类,非常的优雅。
ps: 但是看起来不太舒服,这种写法 c 的风格太强烈了。
/**
* DoubleArrayTrie: Java implementation of Darts (Double-ARray Trie System)
*
* <p>
* Copyright(C) 2001-2007 Taku Kudo <taku@chasen.org><br />
* Copyright(C) 2009 MURAWAKI Yugo <murawaki@nlp.kuee.kyoto-u.ac.jp>
* Copyright(C) 2012 KOMIYA Atsushi <komiya.atsushi@gmail.com>
* </p>
*
* <p>
* The contents of this file may be used under the terms of either of the GNU
* Lesser General Public License Version 2.1 or later (the "LGPL"), or the BSD
* License (the "BSD").
* </p>
*/
package darts;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class DoubleArrayTrie {
private final static int BUF_SIZE = 16384;
private final static int UNIT_SIZE = 8; // size of int + int
private static class Node {
int code;
int depth;
int left;
int right;
};
private int check[];
private int base[];
private boolean used[];
private int size;
private int allocSize;
private List<String> key;
private int keySize;
private int length[];
private int value[];
private int progress;
private int nextCheckPos;
// boolean no_delete_;
int error_;
// int (*progressfunc_) (size_t, size_t);
// inline _resize expanded
private int resize(int newSize) {
int[] base2 = new int[newSize];
int[] check2 = new int[newSize];
boolean used2[] = new boolean[newSize];
if (allocSize > 0) {
System.arraycopy(base, 0, base2, 0, allocSize);
System.arraycopy(check, 0, check2, 0, allocSize);
System.arraycopy(used2, 0, used2, 0, allocSize);
}
base = base2;
check = check2;
used = used2;
return allocSize = newSize;
}
private int fetch(Node parent, List<Node> siblings) {
if (error_ < 0)
return 0;
int prev = 0;
for (int i = parent.left; i < parent.right; i++) {
if ((length != null ? length[i] : key.get(i).length()) < parent.depth)
continue;
String tmp = key.get(i);
int cur = 0;
if ((length != null ? length[i] : tmp.length()) != parent.depth)
cur = (int) tmp.charAt(parent.depth) + 1;
if (prev > cur) {
error_ = -3;
return 0;
}
if (cur != prev || siblings.size() == 0) {
Node tmp_node = new Node();
tmp_node.depth = parent.depth + 1;
tmp_node.code = cur;
tmp_node.left = i;
if (siblings.size() != 0)
siblings.get(siblings.size() - 1).right = i;
siblings.add(tmp_node);
}
prev = cur;
}
if (siblings.size() != 0)
siblings.get(siblings.size() - 1).right = parent.right;
return siblings.size();
}
private int insert(List<Node> siblings) {
if (error_ < 0)
return 0;
int begin = 0;
int pos = ((siblings.get(0).code + 1 > nextCheckPos) ? siblings.get(0).code + 1
: nextCheckPos) - 1;
int nonzero_num = 0;
int first = 0;
if (allocSize <= pos)
resize(pos + 1);
outer: while (true) {
pos++;
if (allocSize <= pos)
resize(pos + 1);
if (check[pos] != 0) {
nonzero_num++;
continue;
} else if (first == 0) {
nextCheckPos = pos;
first = 1;
}
begin = pos - siblings.get(0).code;
if (allocSize <= (begin + siblings.get(siblings.size() - 1).code)) {
// progress can be zero
double l = (1.05 > 1.0 * keySize / (progress + 1)) ? 1.05 : 1.0
* keySize / (progress + 1);
resize((int) (allocSize * l));
}
if (used[begin])
continue;
for (int i = 1; i < siblings.size(); i++)
if (check[begin + siblings.get(i).code] != 0)
continue outer;
break;
}
// -- Simple heuristics --
// if the percentage of non-empty contents in check between the
// index
// 'next_check_pos' and 'check' is greater than some constant value
// (e.g. 0.9),
// new 'next_check_pos' index is written by 'check'.
if (1.0 * nonzero_num / (pos - nextCheckPos + 1) >= 0.95)
nextCheckPos = pos;
used[begin] = true;
size = (size > begin + siblings.get(siblings.size() - 1).code + 1) ? size
: begin + siblings.get(siblings.size() - 1).code + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < siblings.size(); i++)
check[begin + siblings.get(i).code] = begin;
for (int i = 0; i < siblings.size(); i++) {
List<Node> new_siblings = new ArrayList<Node>();
if (fetch(siblings.get(i), new_siblings) == 0) {
base[begin + siblings.get(i).code] = (value != null) ? (-value[siblings
.get(i).left] - 1) : (-siblings.get(i).left - 1);
if (value != null && (-value[siblings.get(i).left] - 1) >= 0) {
error_ = -2;
return 0;
}
progress++;
// if (progress_func_) (*progress_func_) (progress,
// keySize);
} else {
int h = insert(new_siblings);
base[begin + siblings.get(i).code] = h;
}
}
return begin;
}
public DoubleArrayTrie() {
check = null;
base = null;
used = null;
size = 0;
allocSize = 0;
// no_delete_ = false;
error_ = 0;
}
// no deconstructor
// set_result omitted
// the search methods returns (the list of) the value(s) instead
// of (the list of) the pair(s) of value(s) and length(s)
// set_array omitted
// array omitted
void clear() {
// if (! no_delete_)
check = null;
base = null;
used = null;
allocSize = 0;
size = 0;
// no_delete_ = false;
}
public int getUnitSize() {
return UNIT_SIZE;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public int getTotalSize() {
return size * UNIT_SIZE;
}
public int getNonzeroSize() {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (check[i] != 0)
result++;
return result;
}
public int build(List<String> key) {
return build(key, null, null, key.size());
}
public int build(List<String> _key, int _length[], int _value[],
int _keySize) {
if (_keySize > _key.size() || _key == null)
return 0;
// progress_func_ = progress_func;
key = _key;
length = _length;
keySize = _keySize;
value = _value;
progress = 0;
resize(65536 * 32);
base[0] = 1;
nextCheckPos = 0;
Node root_node = new Node();
root_node.left = 0;
root_node.right = keySize;
root_node.depth = 0;
List<Node> siblings = new ArrayList<Node>();
fetch(root_node, siblings);
insert(siblings);
// size += (1 << 8 * 2) + 1; // ???
// if (size >= allocSize) resize (size);
used = null;
key = null;
return error_;
}
public void open(String fileName) throws IOException {
File file = new File(fileName);
size = (int) file.length() / UNIT_SIZE;
check = new int[size];
base = new int[size];
DataInputStream is = null;
try {
is = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(file), BUF_SIZE));
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
base[i] = is.readInt();
check[i] = is.readInt();
}
} finally {
if (is != null)
is.close();
}
}
public void save(String fileName) throws IOException {
DataOutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(fileName)));
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
out.writeInt(base[i]);
out.writeInt(check[i]);
}
out.close();
} finally {
if (out != null)
out.close();
}
}
public int exactMatchSearch(String key) {
return exactMatchSearch(key, 0, 0, 0);
}
public int exactMatchSearch(String key, int pos, int len, int nodePos) {
if (len <= 0)
len = key.length();
if (nodePos <= 0)
nodePos = 0;
int result = -1;
char[] keyChars = key.toCharArray();
int b = base[nodePos];
int p;
for (int i = pos; i < len; i++) {
p = b + (int) (keyChars[i]) + 1;
if (b == check[p])
b = base[p];
else
return result;
}
p = b;
int n = base[p];
if (b == check[p] && n < 0) {
result = -n - 1;
}
return result;
}
public List<Integer> commonPrefixSearch(String key) {
return commonPrefixSearch(key, 0, 0, 0);
}
public List<Integer> commonPrefixSearch(String key, int pos, int len,
int nodePos) {
if (len <= 0)
len = key.length();
if (nodePos <= 0)
nodePos = 0;
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
char[] keyChars = key.toCharArray();
int b = base[nodePos];
int n;
int p;
for (int i = pos; i < len; i++) {
p = b;
n = base[p];
if (b == check[p] && n < 0) {
result.add(-n - 1);
}
p = b + (int) (keyChars[i]) + 1;
if (b == check[p])
b = base[p];
else
return result;
}
p = b;
n = base[p];
if (b == check[p] && n < 0) {
result.add(-n - 1);
}
return result;
}
// debug
public void dump() {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.err.println("i: " + i + " [" + base[i] + ", " + check[i]
+ "]");
}
}
}
参考资料
双数组Trie树(DoubleArrayTrie)Java实现
双数组Trie树(DoubleArrayTrie)Java实现
https://github.com/digitalstain/DoubleArrayTrie
https://linux.thai.net/~thep/datrie/datrie.html
https://www.iteye.com/topic/336577
– 实现
双数组Trie树 (Double-array Trie) 及其应用
https://zekizz.github.io/zi-ran-yu-yan-chu-li/doublearraytrie/
https://midnight2104.github.io/2018/08/08/%E5%8F%8C%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84Trie%E6%A0%91(DoubleArrayTrie)/
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/35193582
https://blog.csdn.net/xlxxcc/article/details/67631988
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoqi/p/Trie.html
http://www.co-ding.com/2012/05/28/DoubleArrayTrie
