# 一、实验概览
lab3实现的是基于代价的查询优化器,以下是讲义给出的实验的大纲:
回想一下,基于成本的优化器的主要思想是:
- 使用有关表的统计信息来估计不同的“成本”
> 查询计划。 通常,一个计划的成本与基数(基数)有关。
>(产生的元组数)中间连接和选择,以及
> 过滤器和连接谓词的选择性。
- 使用这些统计信息对连接和选择进行排序
> 最优方式,并选择加入的最佳实现
> 几种备选方案中的算法。
在本实验中,您将实现代码来执行这两项操作功能。
我们可以使用表的统计数据去估计不同查询计划的代价。
通过这些统计信息,我们可以选择最佳的连接和选择顺序,从多个查询方案中选择一个最佳的计划去执行。
优化器结构概览:
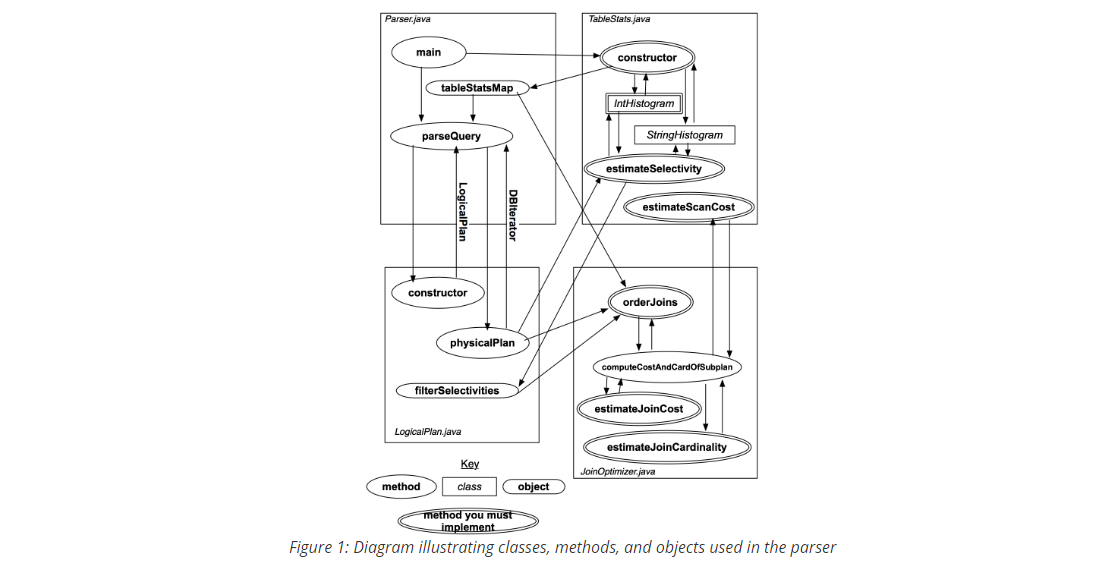
简单总结一下查询优化器的构成:
-
Parser.Java 在初始化时会收集并构造所有表格的统计信息(包括极值, 分桶直方图等等),并存到statsMap中。当有查询请求发送到Parser中时,会调用parseQuery方法去处理
-
parseQuery方法会把解析器解析后的结果去构造出一个LogicalPlan实例,然后调用LogicalPlan实例的physicalPlan方法, 构建一个物理执行计划(也即包含了各种执行算子),然后返回的是结果记录的迭代器,也就是我们在lab2中做的东西都会在physicalPlan中会被调用。
可以看到,lab2我们保证的是一般的SQL语句能够执行;
而在lab3,我们要考虑的事情是怎么让SQL执行得更快,最佳的连接的顺序是什么等待。
个人理解,总体的,lab3的查询优化应该分为两个阶段:
-
第一阶段:收集表的统计信息,有了统计信息我们才可以进行估计;
-
第二阶段:针对 logicalPlan, 生成各种 physicalPlan, 并根据统计信息进行估计每一种 Plan 的代价,找出最优的执行方案。
lab3共有4个exercise,前面两个exercise做的是第一阶段事情,后面两个exercise做的是第二阶段是事情。
除了上面信息,实验的文档outline部分还给出了很多十分有用的信息,告诉我们如何去统计数据,如何去计算代价等等,可以说是指导方针了。
Exercise 1: IntHistogram.java
想要估计查询计划的代价,首先是得有统计数据。
统计直方图
那么数据是怎么从table中获取,以怎样的形式收集并统计呢?
这里用到了直方图。
简单来讲,一个直方图用于表示一个字段的统计信息,直方图将字段的值分为多个相同的区间,并统计每个区间的记录数,每个区间可以看做是一个桶,单个区间的范围大小看成桶的宽,记录数看成桶的宽,可以说是非常的形象:
这里采用了等宽直方图, 还由等深直方图
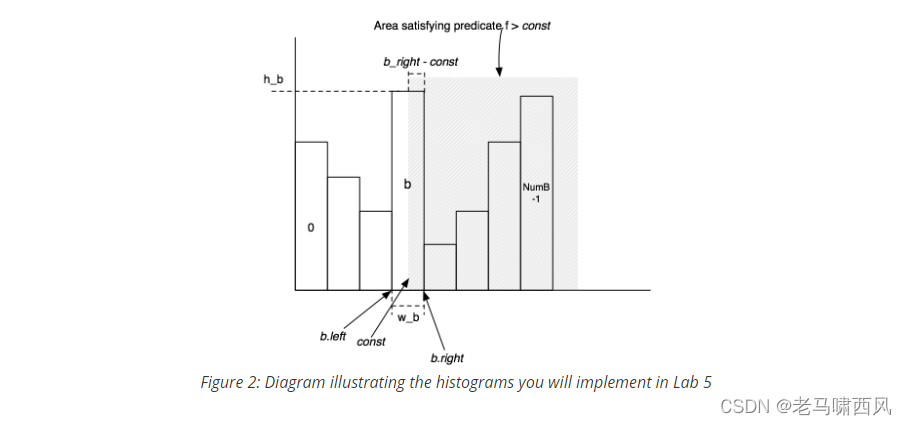
如果看不懂,可以看一下《数据库系统概念》里的图,帆船书里面的图会更容易懂一些。
一张人员信息表格,年龄字段的直方图如下:
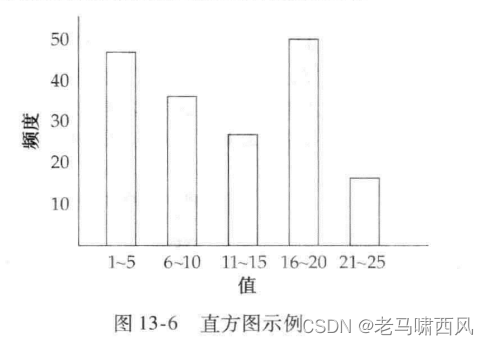
exercise1 要做的就是根据给定的数据字段去构造出这样的直方图,然后是根据直方图的统计信息去估算某个值的选择性(selectivity)。
下面是文档描述信息:
IntHistogram
我们在这个实验只需要实现 IntHistogram ,而 StringHistogram 会将字符串转换为 int 类型然后调用 IntHistogram。
构造器
首先,是构造器与属性部分。
构造器给出直方图的数据范围(最大值最小值),桶的数量。
有了这些信息,就可以构造出一个空的直方图。
/**
* 最大值
*/
private int maxVal;
/**
* 最小值
*/
private int minVal;
/**
* 高度
*/
private int[] heights;
/**
* 桶
*/
private int buckets;
/**
* 总行数
*/
private int totalTuples;
/**
* 宽度
*/
private int width;
/**
* 最新的桶宽度?
*/
private int lastBucketWidth;
对应的构造器如下:
public IntHistogram(int buckets, int min, int max) {
this.minVal = min;
this.maxVal = max;
this.buckets = buckets;
this.heights = new int[buckets];
int total = max - min + 1;
this.width = Math.max(total / buckets, 1);
this.lastBucketWidth = total - (this.width * (buckets - 1));
this.totalTuples = 0;
}
构造的是一个等宽的直方图。
添加值
@Override
public void addValue(Integer v) {
//1. 范围判断
if(v < minVal || v > maxVal) {
return;
}
// 找到值对应的下标(定宽)
int bucketIndex = (v - this.minVal) / this.width;
if (bucketIndex >= this.buckets) {
return;
}
this.totalTuples++;
this.heights[bucketIndex]++;
}
计算某一个值的选择性
接下来是这个 exercise 的大块头,根据直方图已有的统计信息,去计算进行某种运算时某个值表格记录的选择性。
这部分的资料在 outline 很详细的给出如何估计:
等值运算
对于等值运算 f = const,我们要利用直方图估计一个等值表达式f = const的选择性,首先需要计算出包含该const值的桶,然后进行计算:result = (height / width) / totalTuples
可以这样考虑, 我们假设一个桶内的数据是均匀分布的, 比如一个桶由20个记录, 宽为1-5, 那么 const = 3 的记录数就是 20 / 5 = 4,也即利用平均值来进行估算 而 (height / width) / totalTuples 就代表了 const = 3 的数据的在所有记录中的占比
对应实现:
private double estimateEqual(int bucketIndex, int predicateValue, int bucketWidth) {
if (predicateValue < this.minVal || predicateValue > this.maxVal) {
return 0;
}
// As the lab3 doc, result = (bucketHeight / bucketWidth) / totalTuples
return (this.heights[bucketIndex]*1.0 / bucketWidth*1.0) / this.totalTuples*1.0;
}
非等值运算
对于非等值运算,我们采用的也是同样的思想:result = ((right - val) / bucketWidth) * (bucketTuples / totalTuples)
可以这样理解: (right - val) / bucketWidth) 代表了 f > const 在这个桶内的占比
(bucketTuples / totalTuples) 代表了这个桶在所有 tuples 的占比
二者相乘就是这个桶内 f > const 的占比
此外, 还要加上后续每一个桶的占比, 才是最终的 f > const 的结果
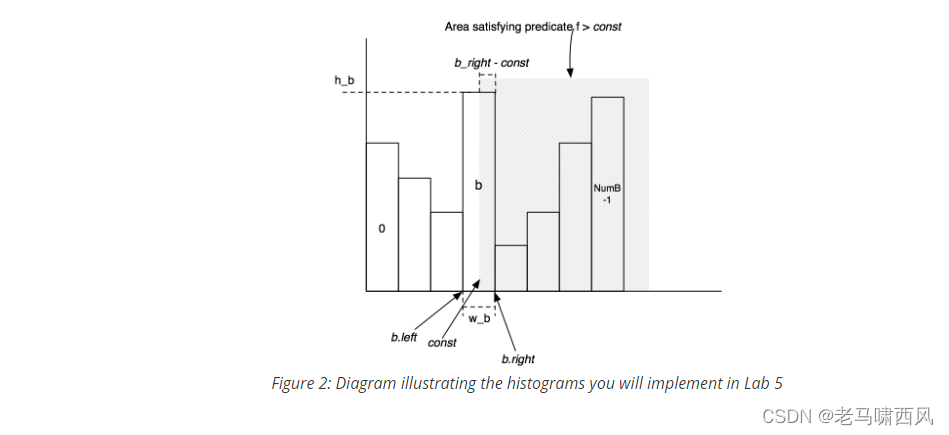
对应实现:
private double estimateGreater(int bucketIndex, int predicateValue, int bucketWidth) {
if (predicateValue < this.minVal) {
return 1.0;
}
if (predicateValue >= this.maxVal) {
return 0;
}
// As the lab3 doc, result = ((right - val) / bucketWidth) * (bucketTuples / totalTuples)
int bucketRight = bucketIndex * this.width + this.minVal;
double bucketRatio = (bucketRight - predicateValue) * 1.0 / bucketWidth;
double result = bucketRatio * (this.heights[bucketIndex] * 1.0 / this.totalTuples);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = bucketIndex + 1; i < this.buckets; i++) {
sum += this.heights[i];
}
return (sum * 1.0) / this.totalTuples + result;
}
完整实现
有了上面的实现之后,我们就可以实现一个相对完整的实现了:
| 符号 | 概率 |
|---|---|
> |
estimateGreater |
= |
estimateEqual |
< |
1 - estimateGreater - estimateEqual |
<= |
1 - estimateGreater |
>= |
estimateGreater + estimateEqual |
实现:
@Override
public double estimateSelectivity(Op op, Integer v) {
final int bucketIndex = Math.min((v - this.minVal) / this.width, this.buckets - 1);
final int bucketWidth = bucketIndex < this.buckets - 1 ? this.width : this.lastBucketWidth;
switch (op) {
case EQUALS:
return estimateEqual(bucketIndex, v, bucketWidth);
case GREATER_THAN:
return estimateGreater(bucketIndex, v, bucketWidth);
case LESS_THAN:
return 1 - estimateGreater(bucketIndex, v, bucketWidth) - estimateEqual(bucketIndex, v, bucketWidth);
case GREATER_THAN_OR_EQ:
return estimateEqual(bucketIndex, v, bucketWidth) + estimateGreater(bucketIndex, v, bucketWidth);
case LESS_THAN_OR_EQ:
return 1 - estimateGreater(bucketIndex, v, bucketWidth);
}
//? 还是0比较合理吧
return -1;
}
StringHistogram
那么字符串类型的统计直方图要怎么实现呢?
我们可以在整数的基础上实现。
只需要将 String 转换为 Integer 即可。
构造器
public class StringHistogram implements Histogram<String> {
/**
* 整数类型的统计直方图
*/
private final IntHistogram hist;
/**
* Create a new StringHistogram with a specified number of buckets.
* <p>
* Our implementation is written in terms of an IntHistogram by converting
* each String to an integer.
*
* @param buckets the number of buckets
*/
public StringHistogram(int buckets) {
hist = new IntHistogram(buckets, minVal(), maxVal());
}
/** @return the maximum value indexed by the histogram */
private int maxVal() {
return stringToInt("zzzz");
}
/** @return the minimum value indexed by the histogram */
private int minVal() {
return stringToInt("");
}
}
字符串转整数
其中字符串与整数的转换如下:
/**
* Convert a string to an integer, with the property that if the return
* value(s1) < return value(s2), then s1 < s2
*/
private int stringToInt(String s) {
int i;
int v = 0;
for (i = 3; i >= 0; i--) {
if (s.length() > 3 - i) {
int ci = s.charAt(3 - i);
v += (ci) << (i * 8);
}
}
// XXX: hack to avoid getting wrong results for
// strings which don't output in the range min to max
if (!(s.equals("") || s.equals("zzzz"))) {
if (v < minVal()) {
v = minVal();
}
if (v > maxVal()) {
v = maxVal();
}
}
return v;
}
其他
其他实现就直接和整数一样了。
@Override
public void addValue(String v) {
Integer integer = stringToInt(v);
hist.addValue(integer);
}
@Override
public double estimateSelectivity(Op op, String v) {
Integer integer = stringToInt(v);
return hist.estimateSelectivity(op, integer);
}
@Override
public double avgSelectivity() {
return hist.avgSelectivity();
}
Exercise 2: TableStats.java
给表创建直方图
exercise2要做的是根据给定的tableid,扫描出所有记录,并对每一个字段建立一个直方图。
下面是outline给出的指导方案:
简单总结一下:
-
扫描全表,把这个表每个字段的值给取出来, 对应函数 fetchFieldValues()
-
对于每个字段, 构建 histogram
实现
构造器
public class TableStats {
/**
* Number of bins for the histogram. Feel free to increase this value over
* 100, though our tests assume that you have at least 100 bins in your
* histograms.
*/
private static final int NUM_HIST_BINS = 100;
// FieldId -> histogram (String or Integer)
private final Map<Integer, Histogram> histogramMap;
/**
* 总行数
*/
private int totalTuples;
/**
* 总页数
*/
private int totalPages;
/**
* 表标识
*/
private int tableId;
/**
* io 每一页的消耗
*/
private int ioCostPerPage;
/**
* 行描述
*/
private TupleDesc tupleDesc;
/**
* Create a new TableStats object, that keeps track of statistics on each
* column of a table
*
* @param tableId The table over which to compute statistics
* @param ioCostPerPage The cost per page of IO. This doesn't differentiate between sequential-scan IO and disk seeks.
*/
public TableStats(int tableId, int ioCostPerPage) {
this.ioCostPerPage = ioCostPerPage;
this.tableId = tableId;
this.histogramMap = new HashMap<>();
this.totalTuples = 0;
final HeapFile table = (HeapFile) Database.getCatalog().getDatabaseFile(tableId);
this.totalPages = table.numPages();
this.tupleDesc = table.getTupleDesc();
}
}
初始化统计直方图
/**
* 初始化统计信息
* 遍历每一个字段,然后初始化对应的统计直方图。
* <p>
* ps: 不要和构造器耦合在一起
*/
public void initHistogramMap() {
//1. 获取所有的字段
Map<Integer, ArrayList> fieldValueMap = fetchFieldValues(tableId);
//2. 构建直方图
for (Map.Entry<Integer, ArrayList> entry : fieldValueMap.entrySet()) {
int fieldIndex = entry.getKey();
ArrayList valueList = entry.getValue();
Type fieldType = tupleDesc.getFieldType(fieldIndex);
if (Type.INT_TYPE.equals(fieldType)) {
final List<Integer> values = (ArrayList<Integer>) valueList;
final int minVal = Collections.min(values);
final int maxVal = Collections.max(values);
//2.1 构造整数直方图
Histogram<Integer> intHistogram = new IntHistogram(NUM_HIST_BINS, minVal, maxVal);
for (Integer integer : values) {
intHistogram.addValue(integer);
histogramMap.put(fieldIndex, intHistogram);
}
} else {
//2.2 构造字符串直方图
Histogram<String> stringHistogram = new StringHistogram(NUM_HIST_BINS);
for (Object object : valueList) {
String string = (String) object;
stringHistogram.addValue(string);
histogramMap.put(fieldIndex, stringHistogram);
}
}
}
}
其中 fetchFieldValues 的实现如下:
/**
* 遍历当前表所有的列
*
* @param tableId 表标识
* @return 结果
*/
private Map<Integer, ArrayList> fetchFieldValues(final int tableId) {
Map<Integer, ArrayList> resultMap = new HashMap<>();
//1. 初始化 map 的类型
for (int i = 0; i < tupleDesc.numFields(); i++) {
Type fieldType = tupleDesc.getFieldType(i);
if (Type.INT_TYPE.equals(fieldType)) {
resultMap.put(i, new ArrayList<Integer>());
} else {
resultMap.put(i, new ArrayList<String>());
}
}
//2. 遍历行
final SeqScan seqScan = new SeqScan(new TransactionId(), tableId);
seqScan.open();
while (seqScan.hasNext()) {
//2.1 遍历行
Tuple tuple = seqScan.next();
this.totalTuples++;
//2. 遍历列
for (int i = 0; i < tupleDesc.numFields(); i++) {
Field field = tuple.getField(i);
Type fieldType = field.getType();
switch (fieldType) {
case INT_TYPE:
int valueInt = ((IntField) field).getValue();
resultMap.get(i).add(valueInt);
break;
case STRING_TYPE:
String valueStr = ((StringField) field).getValue();
;
resultMap.get(i).add(valueStr);
break;
}
}
}
return resultMap;
}
概率计算
那么,获取某一个字段的统计概率实现如下:
/**
* Estimate the selectivity of predicate <tt>field op constant</tt> on the table.
*
* @param field The field over which the predicate ranges
* @param op The logical operation in the predicate
* @param constant The value against which the field is compared
* @return The estimated selectivity (fraction of tuples that satisfy) the predicate
*/
public double estimateSelectivity(int field, Op op, Field constant) {
// some code goes here
if (this.histogramMap.containsKey(field)) {
switch (this.tupleDesc.getFieldType(field)) {
case INT_TYPE: {
final IntHistogram histogram = (IntHistogram) this.histogramMap.get(field);
return histogram.estimateSelectivity(op, ((IntField) constant).getValue());
}
case STRING_TYPE: {
final StringHistogram histogram = (StringHistogram) this.histogramMap.get(field);
return histogram.estimateSelectivity(op, ((StringField) constant).getValue());
}
}
}
return 0.0;
}
表统计的管理类
我们可以针对表统计进行一次管理类实现,以便统一初始化所有的表。
属性
public class TableStatsManager {
private static ConcurrentMap<String, TableStats> STATS_MAP = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static final int IOCOSTPERPAGE = 1000;
//getter & setter
}
初始化概率
遍历所有的表,每一张表调用初始化对应的统计直方图信息。
public static void computeStatistics() {
Iterator<Integer> tableIt = Database.getCatalog().tableIdIterator();
System.out.println("Computing table stats.");
while (tableIt.hasNext()) {
int tableid = tableIt.next();
TableStats s = new TableStats(tableid, IOCOSTPERPAGE);
s.initHistogramMap();
setTableStats(Database.getCatalog().getTableName(tableid), s);
}
System.out.println("Done.");
}
小结
我们想要获取更好的概率,那么首先要做的就是统计。
下一节,我们将一起学习一下如何实现最优概率的选择。
参考资料
https://github.com/CreatorsStack/CreatorDB/blob/master/document/lab2-resolve.md
