LC1466. 重新规划路线 reorder-routes-to-make-all-paths-lead-to-the-city-zero
LC1466. 重新规划路线 reorder-routes-to-make-all-paths-lead-to-the-city-zero
n 座城市,从 0 到 n-1 编号,其间共有 n-1 条路线。因此,要想在两座不同城市之间旅行只有唯一一条路线可供选择(路线网形成一颗树)。去年,交通运输部决定重新规划路线,以改变交通拥堵的状况。
路线用 connections 表示,其中 connections[i] = [a, b] 表示从城市 a 到 b 的一条有向路线。
今年,城市 0 将会举办一场大型比赛,很多游客都想前往城市 0 。
请你帮助重新规划路线方向,使每个城市都可以访问城市 0 。返回需要变更方向的最小路线数。
题目数据 保证 每个城市在重新规划路线方向后都能到达城市 0 。
示例 1:
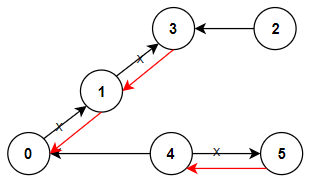
输入:n = 6, connections = [[0,1],[1,3],[2,3],[4,0],[4,5]]
输出:3
解释:更改以红色显示的路线的方向,使每个城市都可以到达城市 0 。
示例 2:
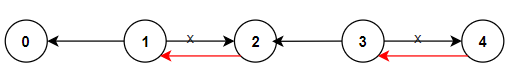
输入:n = 5, connections = [[1,0],[1,2],[3,2],[3,4]]
输出:2
解释:更改以红色显示的路线的方向,使每个城市都可以到达城市 0 。
示例 3:
输入:n = 3, connections = [[1,0],[2,0]]
输出:0
提示:
2 <= n <= 5 * 10^4
connections.length == n-1
connections[i].length == 2
0 <= connections[i][0], connections[i][1] <= n-1
connections[i][0] != connections[i][1]
v1-DFS
思路
这一题题目指定的是有向图,a->b
但是我们想解决问题,实际上要考虑的是从 0 从发,DFS 的无向图。
然后发现如果实际反向和预期的方向相反,说明这个路需要调整。
实现
这里主要是为了方便阅读,所以用来 HashMP+对象的方式
class Solution {
private class Node {
public int target;
public int dir;
public Node(int target, int dir) {
this.target = target;
this.dir = dir;
}
}
// 结果
private int res = 0;
public int minReorder(int n, int[][] connections) {
// 构建无向图
Map<Integer, List<Node>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < connections.length; i++) {
int[] conn = connections[i];
int from = conn[0];
int target = conn[1];
// 顺
Node node1 = new Node(target, 1);
List<Node> list1 = graph.getOrDefault(from, new ArrayList<>());
list1.add(node1);
graph.put(from, list1);
// 逆
Node node2 = new Node(from, 0);
List<Node> list2 = graph.getOrDefault(target, new ArrayList<>());
list2.add(node2);
graph.put(target, list2);
}
// dfs
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
dfs(graph, visited, 0);
return res;
}
private void dfs(Map<Integer, List<Node>> graph, boolean[] visited, int i) {
if(visited[i]) {
return;
}
// 设置
visited[i] = true;
// 邻居
List<Node> ns = graph.get(i);
if(ns != null) {
for(Node node : ns) {
int target = node.target;
if(!visited[target]) {
// 累加
res += node.dir;
dfs(graph, visited, target);
}
}
}
}
}顺路的时候,0->x 说明是从 0 开始顺路,此时是需要+1的。因为预期是期望从 x->0
效果
94ms 击败 12.28%
复杂度
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度(递归栈):O(n)。
反思
复杂度本身并没有毛病。
为什么慢?
引入了对象创建+HashMap
v2-数组
思路
原生的数组性能要比 HashMap 好很多,我们来实现一下。
整体方法不变,知识把 HashMap 改为数组。
实现
class Solution {
private class Node {
public int target;
public int dir;
public Node(int target, int dir) {
this.target = target;
this.dir = dir;
}
}
// 结果
private int res = 0;
public int minReorder(int n, int[][] connections) {
// 构建无向图(j 数组为动态大小)
Node[][] graph = new Node[n][];
int[] degree = new int[n];
for(int[] conn : connections) {
degree[conn[0]]++;
degree[conn[1]]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int size = degree[i];
graph[i] = new Node[size];
}
// 无向图构建
int[] ixArray = new int[n]; // 记录下标
for(int[] conn : connections) {
int from = conn[0];
int target = conn[1];
// 顺
Node node1 = new Node(target, 1);
graph[from][ixArray[from]++] = node1;
// 逆
Node node2 = new Node(from, 0);
graph[target][ixArray[target]++] = node2;
}
// dfs
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
dfs(graph, visited, 0);
return res;
}
private void dfs(Node[][] graph, boolean[] visited, int i) {
if(visited[i]) {
return;
}
// 设置
visited[i] = true;
// 邻居
Node[] ns = graph[i];
if(ns != null) {
for(Node node : ns) {
int target = node.target;
if(!visited[target]) {
// 累加
res += node.dir;
dfs(graph, visited, target);
}
}
}
}
}效果
19ms 击败 98.72%
反思
当然,感觉这里还是有优化空间。
比如这个数组的创建。
v1-Node 替代
思路
当然对象的创建也可以简化,这个是为了方便大家阅读。
Node 完全可以用 int[2] 数组替代
实现
class Solution {
// 结果
private int res = 0;
public int minReorder(int n, int[][] connections) {
// 构建无向图(数组形式)
int[][][] graph = new int[n][][];
int[] degree = new int[n];
// 统计每个节点的度数
for (int[] conn : connections) {
degree[conn[0]]++;
degree[conn[1]]++;
}
// 初始化每个节点的邻接表
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new int[degree[i]][2]; // 每条边存 [target, dir]
}
// 填充邻接表
int[] idx = new int[n]; // 当前下标
for (int[] conn : connections) {
int from = conn[0], to = conn[1];
// 正向边(from -> to),需要翻转
graph[from][idx[from]++] = new int[]{to, 1};
// 反向边(to -> from),不需要翻转
graph[to][idx[to]++] = new int[]{from, 0};
}
// DFS 遍历
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
dfs(graph, visited, 0);
return res;
}
private void dfs(int[][][] graph, boolean[] visited, int u) {
if (visited[u]) return;
visited[u] = true;
for (int[] edge : graph[u]) {
int v = edge[0], dir = edge[1];
if (!visited[v]) {
res += dir;
dfs(graph, visited, v);
}
}
}
}效果
42ms 击败 48.85%
竟然下降了?
猜测原因:
| 版本 | 特性 | 常数开销 |
|---|---|---|
Node[][] | 对象字段访问,JVM 可优化内联 | 较小 |
int[][][] | 三维数组访问 + 多次边界检查 | 稍大 |
ArrayList<int[]>[] | 动态数组,数组引用 + 对象引用 | 介于两者 |
v2-ArrayList 替代 array
思路
数组中有一个 array 的大小计算,很麻烦。
如果用 list 替代,可以不关心。
但是性能略微下降,不过书写时更不容易出错。
实现
class Solution {
private class Node {
public int target;
public int dir;
public Node(int target, int dir) {
this.target = target;
this.dir = dir;
}
}
private int res = 0;
public int minReorder(int n, int[][] connections) {
// 用 ArrayList 替代二维数组
ArrayList<Node>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 构建图
for (int[] conn : connections) {
int from = conn[0], to = conn[1];
// 正向边 (from -> to) 需要翻转
graph[from].add(new Node(to, 1));
// 反向边 (to -> from) 不需要翻转
graph[to].add(new Node(from, 0));
}
// DFS
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
dfs(graph, visited, 0);
return res;
}
private void dfs(ArrayList<Node>[] graph, boolean[] visited, int u) {
visited[u] = true;
for (Node node : graph[u]) {
int v = node.target;
if (!visited[v]) {
res += node.dir;
dfs(graph, visited, v);
}
}
}
}效果
31ms 击败 95.91%
实际比赛,还是推荐大家用 list 的方式,避免踩坑。
